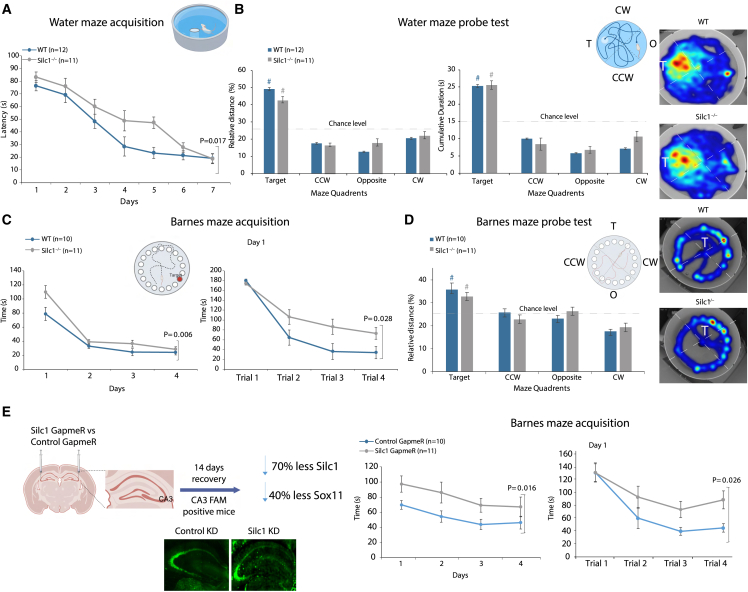
Figure 5.
Silc1−/− reduction delays spatial learning
(A) Escape latencies (in seconds) over MWM training sessions; compared with the WT (n = 12), Silc1−/− (n = 11) mice exhibited significantly slower learning (gene [main effect]: F(1,22) = 6.712, p = 0.017).
(B) Probe test session (24 h after the last acquisition session). Left: relative distance swum (%). center: cumulative duration (seconds) per quadrant. Right: grouped heatmaps (cumulative duration). Probe test data indicated that Silc1−/− and WT mice explored the target quadrant significantly more than chance level (#; one-sample t test: relative distance [%]: WT t(11) = 8.737; p = 0.000. Silc1−/− t(10) = 10.021; p = 0.000. Cumulative duration (seconds): WT t(11) = 7.359; p = 0.000. Silc1−/− t(10) = 8.400; p = 0.000) in a similar manner (WT vs. Silc1−/−: relative distance [%]: t(21) = 1.849; p = 0.079. Cumulative duration (seconds): t(21) = 0.137; p = 0.893).
(C) Escape latencies (seconds) in the Barnes maze over daily training sessions (left) and within trials of day 1 (right) compared with WT (n = 10) and Silc1−/− mice (n = 11) exhibited significantly slower learning (gene [main effect]: over days F(1,19) = 9.484; p = 0.006. Day1 F(1,19) = 5.682; p = 0.028).
(D) Probe test session (24 h after the last acquisition session). Left: relative distance swum (%). Right: grouped heatmaps (cumulative duration). Probe test data indicated that Silc1−/− and WT mice explored the target quadrant significantly more than chance level (#: one-sample t test: relative distance [%]: WT t(9) = 3.697; p = 0.005. Silc1−/− t(10) = 4.246; p = 0.002) in a similar manner (WT vs. Silc1−/−: relative distance [%]: t(19) = 0.882; p = 0.389).
(E) Barnes maze escape latencies (in seconds) over daily training sessions (left) and within trials of day 1 (right) of WT C57BL/6 mice injected with Silc1 GapmeR (n = 12) or control GapmeR (n = 10) indicated that knockdown of Silc1 impairs learning (gene [main effect]: over days F(1,20) = 6.943 = 0.016. Day 1 F(1,20) = 5.801; p = 0.026).
Data represent mean ± SEM (error bars). All datasets were analyzed by two-way ANOVA for gene (between subjects), daily training sessions/trials (within subjects with repeated measures), and their interaction (gene × training). Images were generated using BioRender. See also Figure S5.