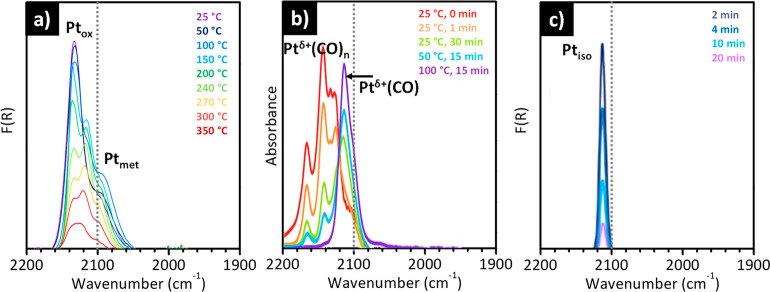
Figure 17.
In situ IR spectroscopy of adsorbed CO allows the discrimination of isolated Pt sites from oxidized clusters. (a) IR spectra collected at different temperatures during a CO-TPD experiment in He performed on a 1 wt % Pt/TiO2 catalyst obtained via incipient wetness impregnation that was preoxidized for 2 h in air at 300 °C. CO desorbs from Ptox sites at higher temperature than from Pt metal sites, with significant desorption only above 200 °C and incomplete desorption even by 350 °C. Adapted with permission from ref (290). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society. (b) IR spectra collected at different temperatures during a CO-TPD experiment in Ar performed on a 0.5 wt % Pt/HZSM-5 sample prepared by solution grafting of a Pt organometallic complex. Cationic Ptδ+-polycarbonyl species are easily converted into Ptδ+-monocarbonyls already at room temperature, the latter being stable at 100 °C. Adapted with permission from ref (207). Copyright 2015 American Association for the Advancement of Science. (c) IR spectrum of CO adsorbed at room temperature on a prereduced 0.05 wt % Pt/TiO2 catalyst prepared according to a synthetic protocol, which allows the deposition of less than 1 Pt atom per TiO2 particle, and its evolution upon desorption in inert atmosphere at room temperature. Adapted with permission from ref (290). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society.