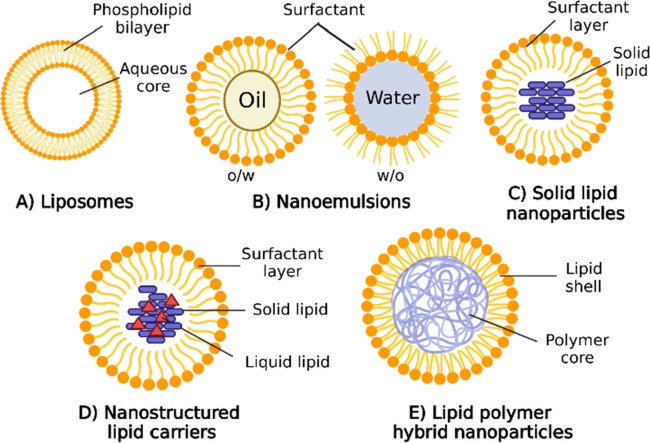
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration depicts the structure of various LNP formulations used in drug delivery. (A) Liposomes are spherical vesicles with phospholipid bilayers, encapsulating hydrophilic drugs in their aqueous core and incorporating hydrophobic drugs within the lipid bilayers. (B) Nanoemulsions comprise oil droplets dispersed in an aqueous phase stabilized by surfactants, accommodating lipophilic drugs in the oil phase while preventing droplet aggregation. (C) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) consist of solid lipid matrices entrapping hydrophobic drugs, forming nanoscale particles with a lipid core. (D) Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) are similar to SLNs but contain a combination of solid and liquid lipids, resulting in a more stable matrix and improved drug loading capacity. (E) Lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles combine lipid-based and polymer-based components, offering the benefits of both systems. These nanoparticles can effectively encapsulate various types of drugs and exhibit enhanced stability and controlled release properties. Each type of LNP structure provides unique advantages and can be tailored for targeted drug delivery, enabling the encapsulation of a diverse range of therapeutic agents. Figure created with BioRender.com.