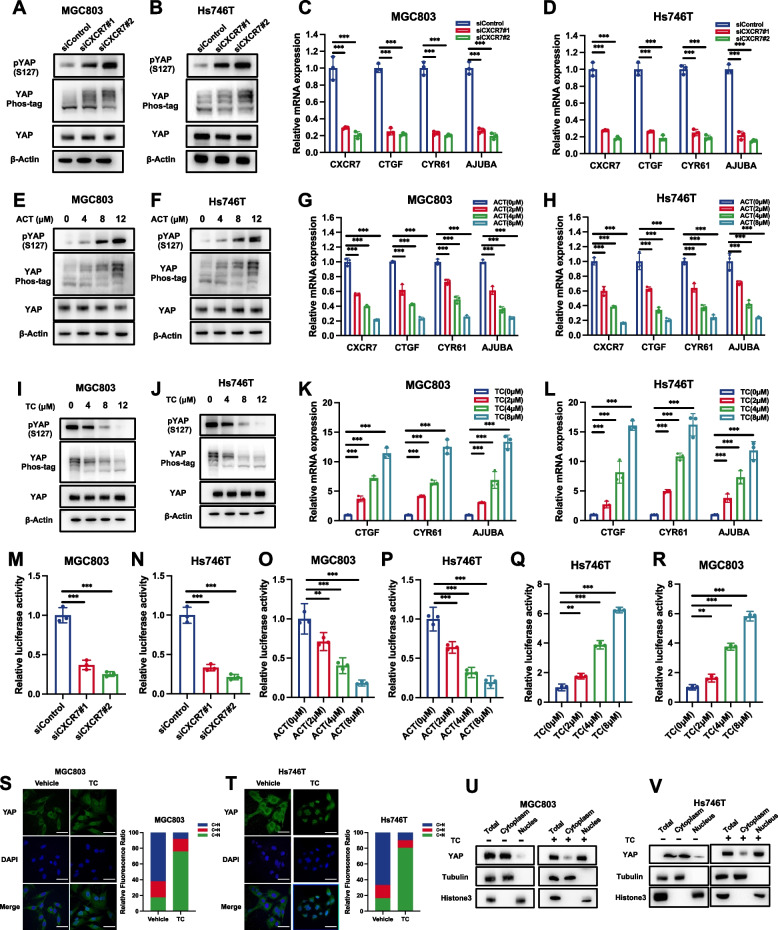
Fig. 5.
CXCR7 activates the YAP axis by inducing YAP dephosphorylation. A, B CXCR7 depletion in MGC803 and Hs746T cells induced YAP phosphorylation as determined by immunoblotting with S127 phospho-antibody and phospho-tag assay. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were transfected with different siCXCR7s. Immunoblotting was performed with the indicated antibodies. Phos-tagged gels were used to assess the phosphorylation status of YAP. C, D CXCR7 depletion decreased Hippo target gene expression in MGC803 and Hs746T cells. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were transfected with siControl or siCXCR7. After 48 h, total RNA was extracted for gene expression analysis. Each group was tested in triplicate. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 for comparisons of target gene expression. E, F Antagonist ACT treatment against CXCR7 induced YAP phosphorylation as determined by immunoblotting with S127 phospho-antibody and phospho-tag assay. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were transfected with different doses of ACT as indicated. Immunoblotting was performed with the indicated antibodies. Phos-tagged gels were used to assess the phosphorylation status of YAP. G, H ACT antagonist treatment against CXCR7 decreased Hippo target gene expression in MGC803 and Hs746T cells. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were treated with different doses of ACT as indicated. Total RNA was extracted for gene expression analysis. Each group was tested in triplicate. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 for comparisons of target gene expression. I, J CXCR7 activation via TC induced YAP dephosphorylation as determined by immunoblotting with S127 phospho-antibody and phospho-tag assay. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were transfected with different doses of TC as indicated. Immunoblotting was performed with the indicated antibodies. Phos-tagged gels were used to assess the phosphorylation status of YAP. K, L CXCR7 activation via TC increased Hippo target gene expression in MGC803 and Hs746T cells. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were treated with different doses of TC as indicated. Total RNA was extracted for gene expression analysis. Each group was tested in triplicate. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 for comparisons of target gene expression. M, N CXCR7 depletion in MGC803 and Hs746T cells decreased TEAD response element activity. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were transfected with siControl or siCXCR7. After 24 h, the cells were transfected with TEAD luciferase reporter plasmids. After another 24 h, the cells were harvested for luciferase activity analysis. O, P CXCR7 blockage via ACT in MGC803 and Hs746T cells decreased TEAD response element activity. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were transfected with different doses of ACT as indicated. After 24 h, the cells were transfected with TEAD luciferase reporter plasmids. After another 24 h, the cells were harvested for luciferase activity analysis. Q, R CXCR7 activation via TC increased TEAD response element activity. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were transfected with different doses of TC as indicated. After 24 h, the cells were transfected with TEAD luciferase reporter plasmids. After another 24 h, the cells were harvested for luciferase activity analysis. S, T TC promotes YAP translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. MGC803 and Hs746T cells were stimulated with different doses of TC as indicated. Endogenous YAP (green) and nuclei (blue) were stained with specific antibodies and DAPI, respectively; scale bar, 20 mm. Quantifications of YAP subcellular localization from at least 100. C, cytoplasm; N, nucleus. U, V Nucleoplasm separation experiments by immunoblotting confirmed that TC induced YAP protein translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in MGC803 and Hs746T cells