Fig 1.
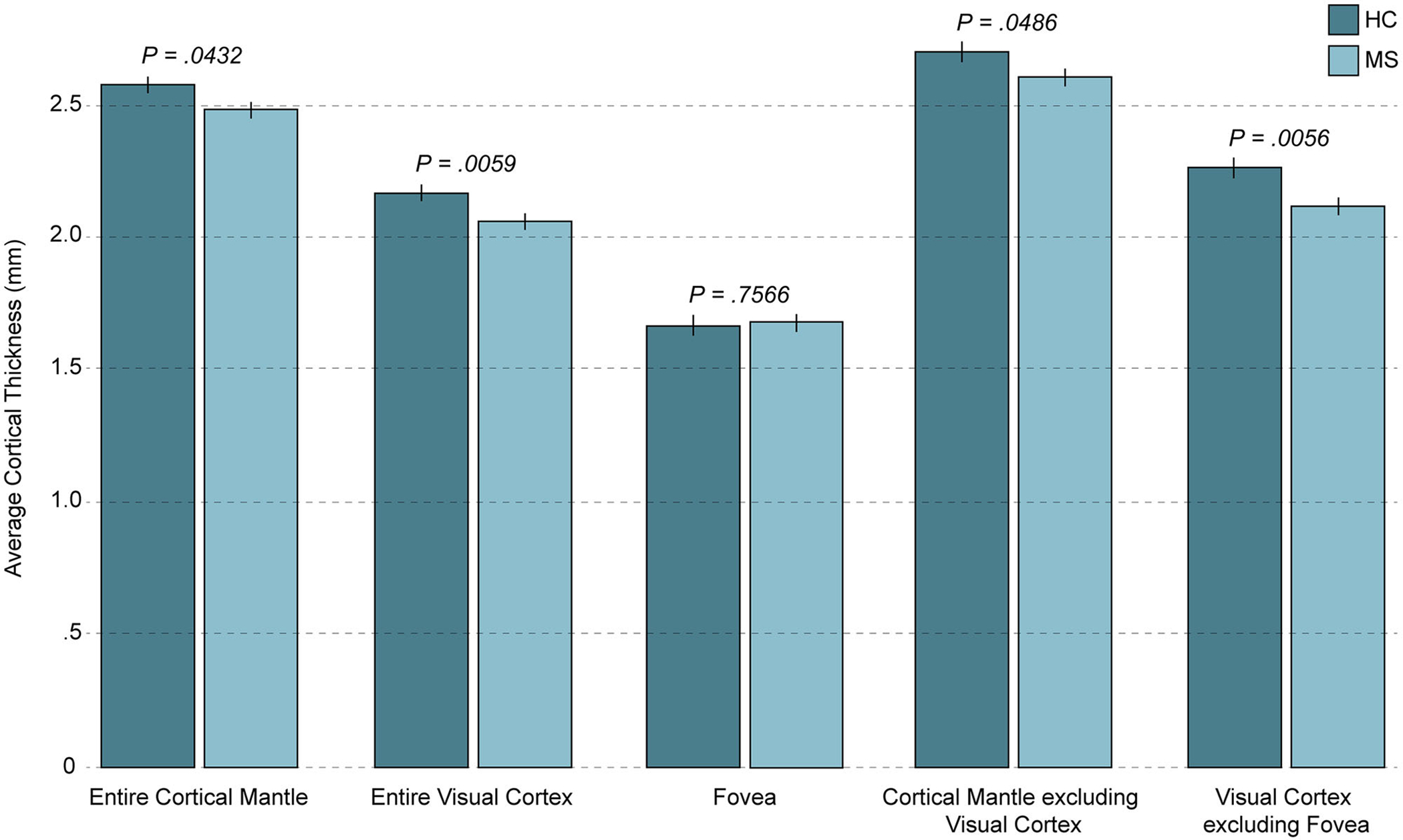
Cortical mantle thickness in pediatric-onset MS and healthy controls. The average cortical thicknesses for the mean of the left and right hemispheres are shown for pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis (POMS) patients and healthy controls, and Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted P-values (corrected for multiple comparisons) are indicated. POMS patients demonstrated significant thinning of the entire cortical mantle, the entire visual cortex, the cortical mantle excluding the visual cortex, and the visual cortex excluding the fovea; however, the foveal confluence was spared. Thinning of the visual cortex significantly accounted for the difference between POMS patients and controls when the cortical mantle was considered as a whole. HC = healthy control; MS = multiple sclerosis.
