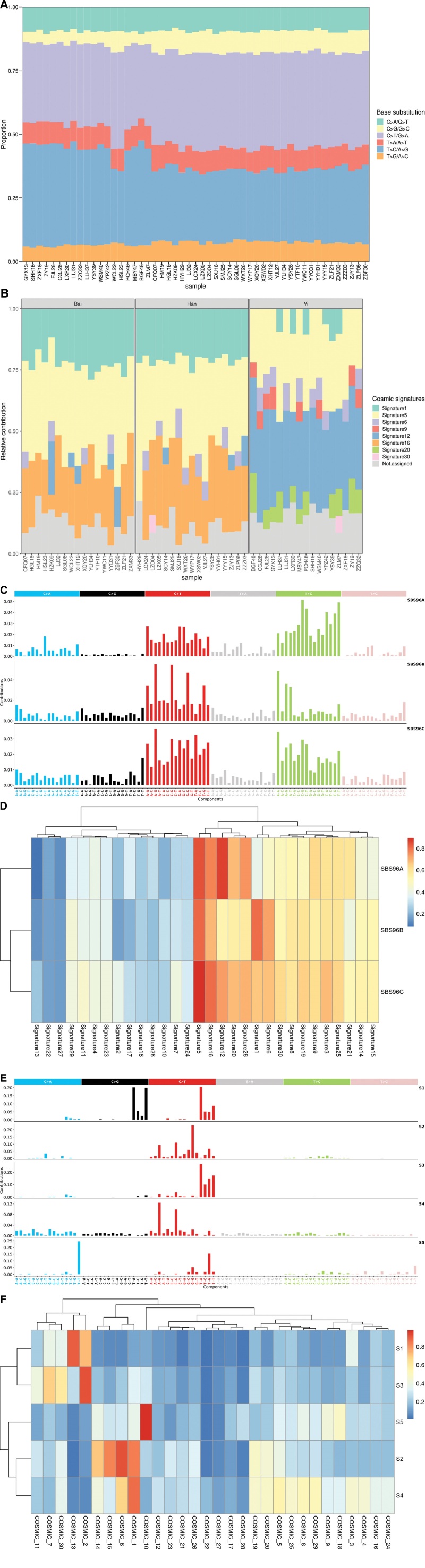
Figure 2.
The mutation spectrums and mutational signatures in CIN2/3. (A) Distribution of 6 base substitution types in 51 CIN2/3. The x-axis indicated the patients ID, and the y-axis depicted the proportion of each mutation categories. (B) Mutational signature profiles identified with deconstructSigs tool in 51 CIN2/3. The x-axis indicated the patients ID, and the y-axis showed the proportion of each mutational signatures. (C) De novo mutational signatures identified with SigProfilerExtractor tool in 51 CIN2/3. (D) Heatmap of cosine similarity between extracted de novo mutational signatures in CIN2/3 and COSMIC v2 reference mutational signatures. (E) De novo mutational signatures identified with SigProfilerExtractor tool in TCGA-CESC. (F) Heatmap of cosine similarity between extracted de novo mutational signatures in TCGA-CESC and COSMIC v2 reference mutational signatures. CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; TCGA-CESC, the Cancer Genome Atlas cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma.