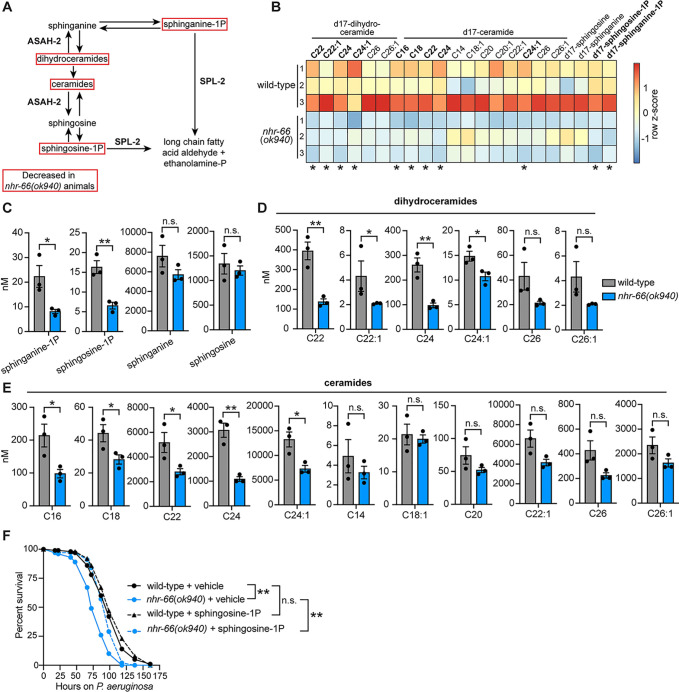
Fig 4. Sphingolipid degradation in nhr-66(ok940) mutants compromises survival during pathogen infection.
A. Schematic of sphingolipid metabolism in C. elegans. B. Heatmap of HPLC-MS/MS data depicting the concentrations of d-17 ceramides and di-17 dihydroceramides normalized to total protein levels. The expression level was scaled in each condition by calculating a row z-score for each lipid species *p<0.05 (Student’s unpaired t-test) C–E. The concentrations of the indicated sphingolipids in wild-type versus nhr-66(ok940) animals as measured by HPLC-MS/MS. n = 3 biological replicates, * p<0.05, **p<0.01 (Student’s unpaired t-test), n.s. (not significant). F. C. elegans-P. aeruginosa pathogenesis assay with C. elegans of indicated genotypes at the L4 larval stage are shown. The difference in survival between nhr-66(ok940) mutants and other conditions is significant ** p<0.01 (log-rank test). Data representative of three biological replicates (n = 3). Sample sizes, mean lifespan, and p-values for each replicate of this pathogenesis assay are in S5 Table. The source data for this figure is in S6 Table.