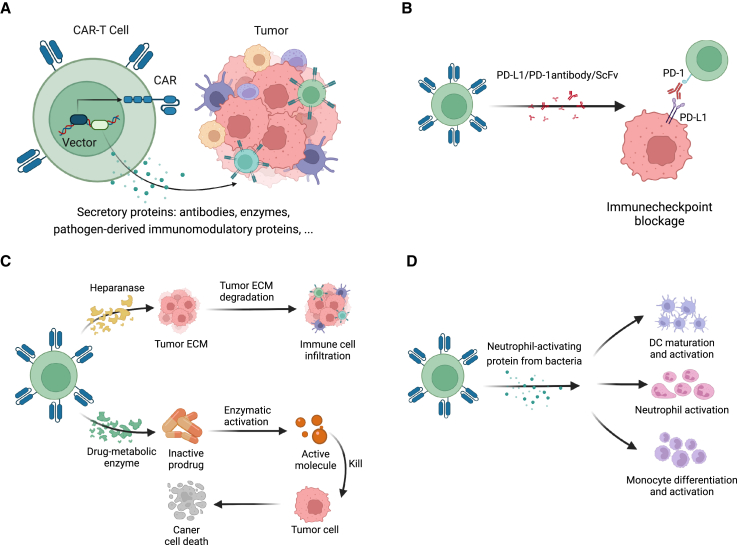
Figure 2.
Engineering CAR-T cells as vehicles to secrete antitumor proteins into TME
(A) Armored CAR-T cells engineered to release a variety of secretory proteins to enhance their antitumor capacity. (B) Representatives of antibodies and ScFvs that armored CAR-T cells can generate, the functions of which include immunocheckpoint blockage (PD-1/PD-L1 antibody/ScFv). (C) Representative enzymes that armored CAR-T cells secrete, which can degrade ECM to improve infiltration (HPSE) or convert prodrugs to cytotoxic agents in situ (drug-metabolic enzyme). (D) Representative pathogen-derived immunomodulatory protein that CAR-T cells release (neutrophil-activating protein from H. pylori), which activates various innate immune cells in TME.