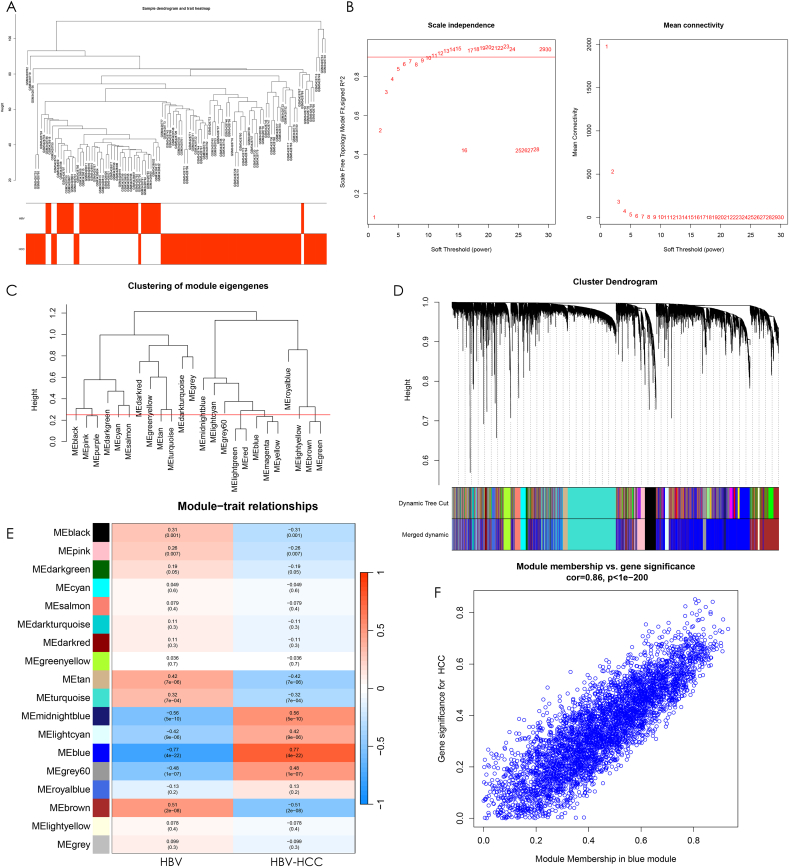
Fig. 3.
Construction of gene co-expression network. (A) Cluster tree with heat map display for all samples in the training set, and the cluster tree samples corresponding to the red heat map belong to this clinical trait. (B) The left panel is set when the scale-free topological fit index R^2 = 0.9, and the best soft threshold β = 9 is chosen to obtain the best average connectivity of the co-expression network on the right panel. (C) The clustering height was set to 0.25 and the modules were clipped. The modules with high gene similarity were merged together to get 18 modules. (D) Sample clustering tree with the modules before and after merging, Dynamic Tree Cut for the original modules and Merged dynamic for the result after merging the strongly associated modules. (E) Heat map of correlations between modules and clinical traits. Red indicates positive correlation, blue indicates negative correlation, and the darker the color, the stronger the correlation. The numbers in parentheses are the p-values of correlations between modules and traits to test whether they are statistically significant with each other. The numbers above the brackets indicate the magnitude of correlation between modules and traits. (F) Scatter plot between blue module affiliation and HBV-HCC gene significance with a correlation between each other of cor = 0.86,p < 1e-200.