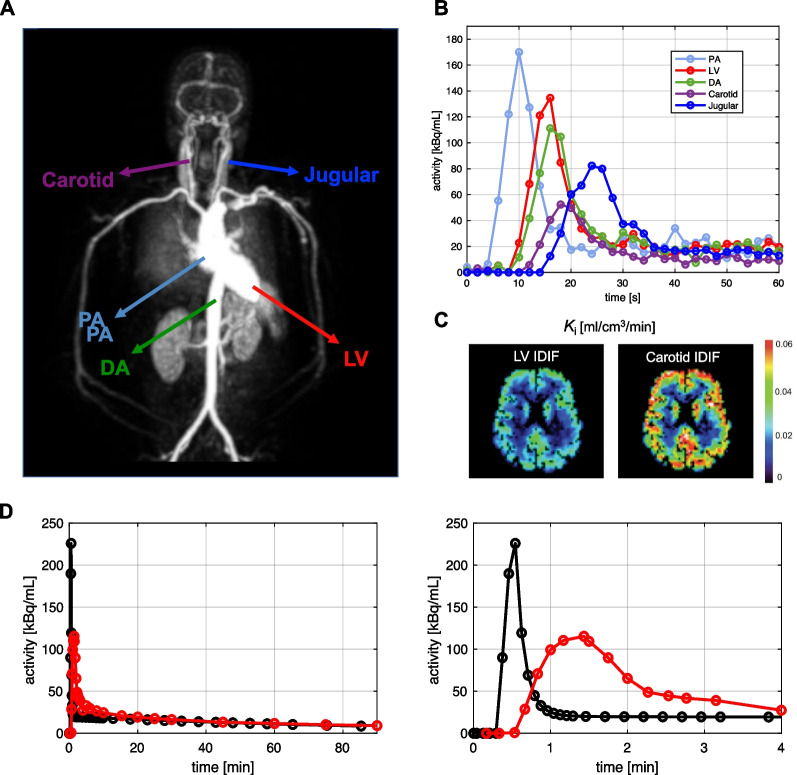
Fig. 6.
Comparing delay and dispersion of multiple IDIF sites. Impact of IDIF extraction site on input delay/dispersion and kinetic parameter estimates, specifically [18F]FDG Ki in the brain. Total-body PET maximum intensity projection image of different vascular sites for IDIF extraction, i.e., pulmonary artery (PA, ~ 3 cm), left ventricle (LV, ~ 4 to 6 cm), descending aorta (DA, ~ 2.5 to 3 cm), common carotid arteries (~ 7 mm), jugular veins (~ 0.8 to 1.2 cm) (A). Simulated IDIF curves representing the delay/dispersion characteristics of each site (B). Ki parametric maps (brain), showing how Ki is higher for the carotid IDIF due to the smaller IDIF AUC with respect to the LV (C). Differences in delay and dispersion between IDIF extracted from the aorta (black) and AIF obtained from radial artery (red) in a simulated [18F]FDG PET study; the full-time course is shown on the left, and the first four minutes on the right (D)