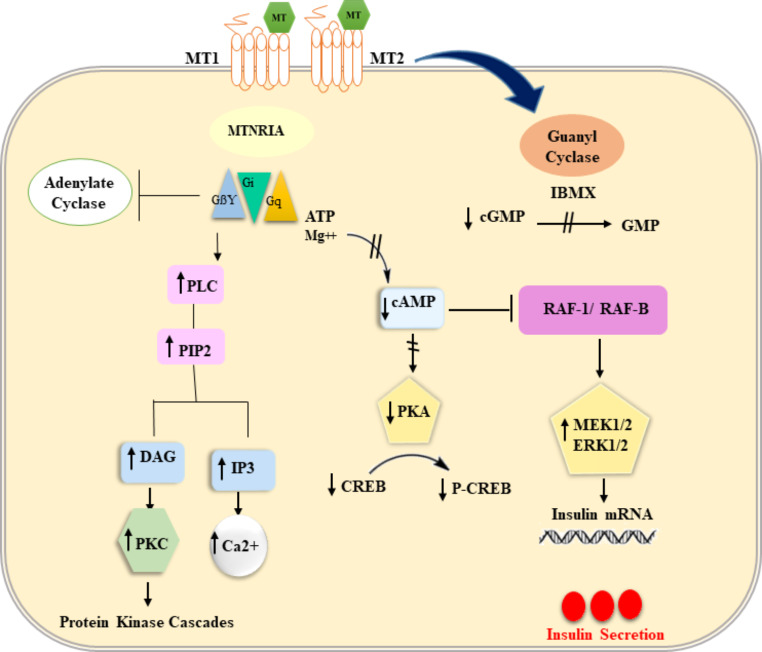
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of the membrane signaling by melatonin receptors MT 1 and MT 2. In part of the figure is shown the interaction of Gi with adenyl cyclase (AC) to decrease cAMP levels and therefore cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity (PKA) and interaction of G q with phospholipase C (PLC) leading to the cleavage of phosphatidyl inositol diphosphate (PIP2) into inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). These second messengers stimulate increased intracellular Ca2 + and protein kinase C (PKC), respectively. In another part of the figure is shown the melatonin/MTNR/Raf-1/ERK signaling pathway. Melatonin binds to the MT2 receptor followed by reduced cAMP production and PKA inhibition. In turn, this inactivates the Ras/Raf-1/ERK pathway, eventually decreasing insulin gene transcription. (Original figure by the authors)