Fig. 8. Schematic depiction of the mechanism by which MELK promotes HCC carcinogenesis through modulating DLAT-mediated mitochondrial function.
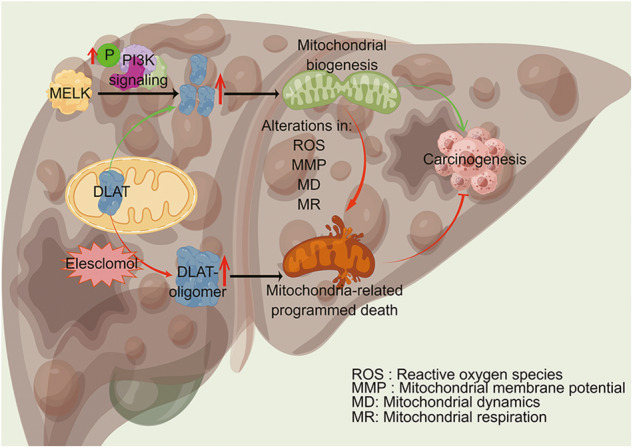
MELK augments the expression of the CRS gene DLAT through the PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway and promotes mitochondrial function, which subsequently promotes the progression of HCC. Abnormal expression of MELK impaired mitochondrial function through alterations in ROS, MMP, MD and MR. The copper ionophore (elesclomol) increased DLAT oligomer (which inhibits the function of DLAT oncogene and leads to cuproptosis), inducing mitochondria-related programmed death, and subsequently inhibiting the progression of HCC. In all, evidence described above showed that the cuproptosis-associated pathway was essential in MELK-induced HCC progression. *Figure was drawn by Figdraw(WIWWAacf4a).
