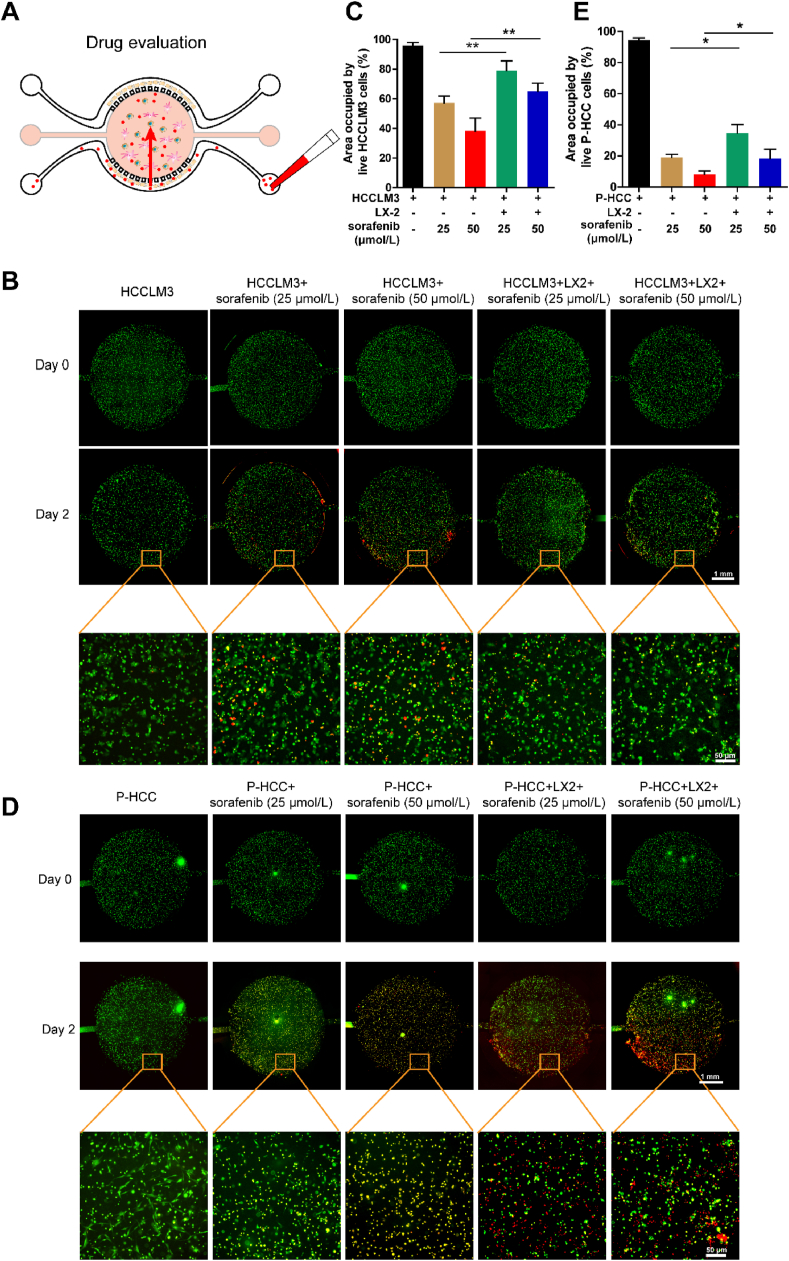
Figure 3.
Assessment of Sorafenib resistance via chip. (A) Schematic representation of drug killing effects on liver cancer cells in the HCC-on-a-chip model. The HCCLM3 cells (labeled in green) were cultured with or without LX2 in the HCC-on-a-chip model for 3 days, then specific drugs were added from one side channel of the chip to investigate the tumor cell killing effect at different concentrations. After 48 h, the PI was added at the same channel to label the dead cells. (B) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of live/dead HCCLM3 cells were shown in the chip after the treatment of sorafenib for 2 days. Scale bar: 1 mm. (C) Quantification of the area occupied by the live HCCLM3 cells (green) in the indicated groups from B (n = 5 per group). (D) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of live/dead patient-derived liver cancer cells (green) were shown in the chip after the treatment of sorafenib for 2 days. (E) Quantification of the area occupied by the patient-derived liver cancer cells (green) in indicated groups from D (n = 3 per group). Scale bar: 1 mm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01.