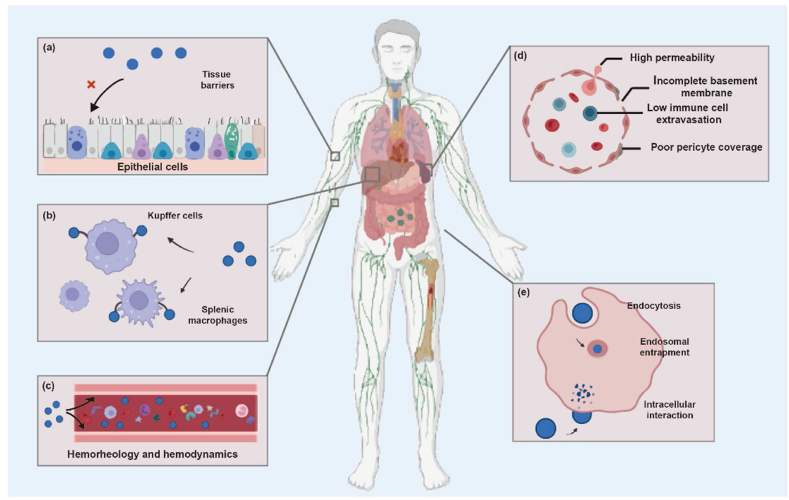
Figure 8.
Sequential in vivo processes that nanomedicines may go through: (a) interactions with the tissue barriers that prevent nanomedicines from entering into the body; (b) uptake of nanomedicines by the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS); (c) hemorheological and hemodynamic disposition of nanomedicines which alters the integrity, kinetics, and interaction with hematic components; (d) post-MPS distribution and disposition of nanomedicines by specialized physiological mechanisms such as passive tumor targeting owing to the EPR effect; (e) endosomal compartmentalization and cell membrane trafficking of nanomedicines. Adapted with permission from Ref. 183. Copyright©2022 Elsevier.