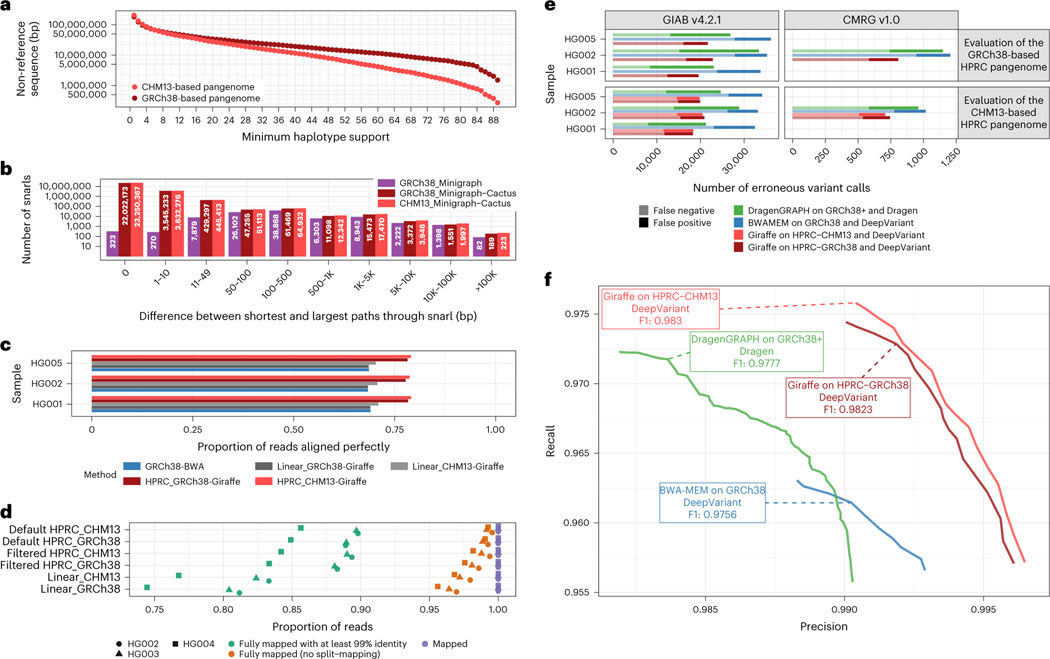
Fig. 2 |. Evaluating GRCh38-based and T2T-CHM13-based human pangenomes.
a, The amount of non-reference sequence in the HPRC graphs by the minimum number of haplotypes it is contained in. b, Distribution of the size of the snarls (variation sites, also known as bubbles) for the GRCh38-based minigraph and GRCh38-based and CHM13-based Minigraph-Cactus pangenomes. Note that, in the case of overlapping variants, snarls can be much larger than any single event that they contain. c,e,f, ~30× Illumina short reads for three GIAB samples were mapped using three approaches: BWA-MEM on GRCh38 (blue), vg Giraffe on the linear pangenomes with GRCh 38 or CHM13 (gray) and vg Giraffe on the GRCh38-referenced or CHM13-referenced HPRC pangenome (red). c, Proportion of the reads aligning perfectly to the (pan-)genome for each sample (y axis). d, Number of Hi-Fi reads mapped to the linear, filtered and default (unfiltered by allele frequency) pangenomes. For each sample and pangenome, three points show the number of mapped reads (purple square), reads mapped without being split (orange triangle) and reads fully mapped with at least 99% identity. e,f, Short variants were called with DeepVariant after projecting the reads to GCRh38 from the GRCh38-based pangenome (dark red) or the CHM13-based pangenome (light red). The results when aligning reads with BWA-MEM (blue) or using the Dragen pipeline (green) are also shown. e, The number of erroneous calls (false positive in dark, false negative in pale) is shown on the x axis across samples from GIAB (y axis). Left: GIAB version 4.2.2 high-confidence calls. Right: CMRG version 1.0. When evaluating the CHM13-based pangenome (bottom panels), regions with false duplications or collapsed in GRCh38 were excluded. f, The graph shows the precision (x axis) and recall (y axis) for different approaches using the CMRG version 1.0 truth set for the HG002 sample (bottom-right panel in e). The curves are traced by increasing the minimum quality of the calls.