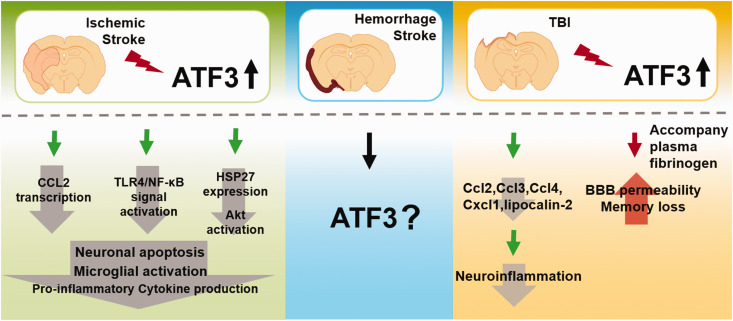
Figure 2.
The function of ATF3 on acute brain injury. In the ischemic stroke, ATF3 overexpression attenuated neuronal caspase-dependent apoptosis, microglial activation, and pro-inflammatory cytokine production to alleviate brain injury. ATF3 can block CCL2 transcription and TLR4/NF-κB signal activation to reduce the activation of microglia and prevent neuronal apoptosis. Another is to prevent neuronal apoptosis induced by c-Jun N-terminal kinase by promoting the expression of the anti-apoptotic neuronal survival factor HSP27 and activation of Akt. There is a lack of knowledge regarding the regulation of ATF3 in hemorrhagic stroke. In TBI, upregulation of ATF3 in the brain negatively regulates CCL and CXCL chemokines (Ccl2, Ccl3, Ccl4, and Cxcl1) and lipocalin-2 expression, which then alleviates neuroinflammation after TBI. But increased BBB permeability and loss of memory after TBI are both caused by Fg-induced overexpression of ATF3.
TLR: toll like receptor; HSP: heat shock protein; TBI: traumatic brain injury; Ccl: C-C motif ligand; Cxcl: CXC chemokine ligand; Fg: plasma fibrinogen; BBB: blood brain barrier.