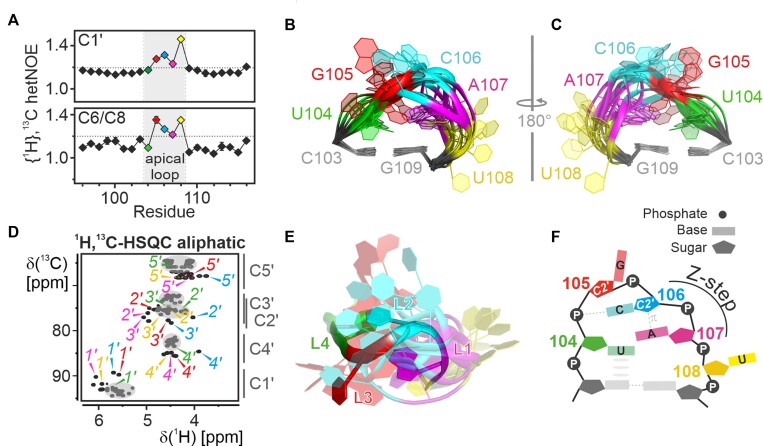
Figure 3.
Structural details of the apical loop. (A) {1H},13C-hetNOE of the aromatic pyrimidine H6C6 and the purine H8C8 moieties (bottom) and aliphatic H1’C1’ moieties (top) of 5_SL4sh. Residues of the loop region (gray) are highlighted in different colors according to the color scheme in Figure 2. A dashed line indicates the threshold for flexible residues (1.2). (B-C) NMR structural bundle of the apical loop. The loop closing base pair is used for structure alignment. The RNA is shown as a cartoon representation in two different orientations turned by 180° in respect to each other. The loop residues shown in different colors according to the color scheme in Figure 2 and assigned. (D) Aliphatic 1H,13C-HSQC of 5_SL4sh. Resonances of U104 (green), G105 (red), C106 (blue) and A107 (magenta) are assigned in the respective colors. Gray spheres mark the canonical regions of the spectrum and characteristic 13C chemical shift regions are indicated to the right of the graph. (E) Overlay between the apical loop region of the NMR bundle of 5_SL4 and the lowest target function NMR structure of the cUUCGg tetraloop in a 14-nt RNA stem-loop (PDB entry 2koc). The C-G closing base pairs are used for alignment of the loops. The 5_SL4 RNA is shown as a cartoon representation using the color scheme shown in Figure 2. The UUCG tetraloop residues are colored accordingly. (F) Schematic representation of the transient structural features of the 5_SL4 apical loop. Residues are highlighted in different colors according to the color scheme in Figure 2 and assigned. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines and stacking interactions as gray ellipses. The Z-step with its lone pair...π stacking contact is indicated.