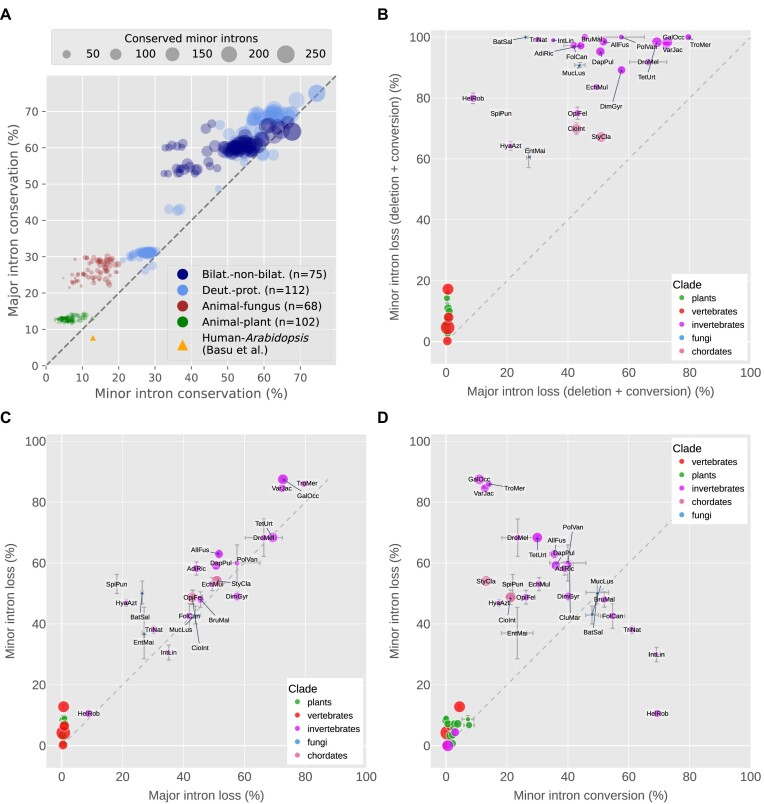
Figure 3.
Conservation and loss of minor and major introns. (A) Comparison of major (y-axis) versus minor (x-axis) intron conservation across hundreds of pairs of species. Bilat.-non-bilat.: bilaterian versus non-bilaterian (animal); Deut.-prot.: deuterostome versus protostome. The yellow triangle indicates levels of conservation of major and minor introns between Homo sapiens and Arabidopsis thaliana as reported by Basu et al. (74). Size of markers indicates number of minor introns conserved between each pair. (B) Minor versus major intron loss, where ‘loss’ includes both sequence deletion and conversion to an intron of the other type. Bars indicate standard error of the mean for averaged values. Marker size represents relative minor intron density. (C) Minor versus major intron loss, where ‘loss’ represents actual deletion of the intron sequence. (D) Minor intron loss versus conversion, where ‘loss’ represents actual deletion of the intron sequence. Species abbreviations for are as follow: AdiRic: Adineta ricciae, AllFus: Allacma fusca, BatSal: Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans, BruMal: Brugia malayi, CioInt: Ciona intestinalis, CluMar: Clunio marinus, DapPul: Daphnia pulicaria, DimGyr: Dimorphilus gyrociliatus, DroMel: Drosophila melanogaster, EchMul: Echinococcus multilocularis, EntMai: Entomophaga maimaiga, FolCan: Folsomia candida, GalOcc: Galendromus occidentalis, HelRob: Helobdella robusta, HyaAzt: Hyalella azteca, IntLin: Intoshia linei, MucLus: Mucor lusitanicus, OpiFel: Opisthorchis felineus, PolVan: Polypedilum vanderplanki, SpiPun: Spizellomyces punctatus, StyCla: Styela clava, TetUrt: Tetranychus urticae, TriNat: Trichinella nativa, TroMer: Tropilaelaps mercedesae, VarJac: Varroa jacobsoni.