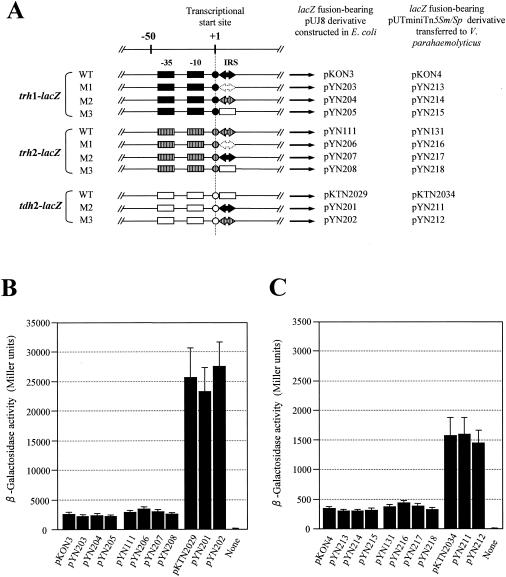
FIG. 3.
Transcriptional levels of the trh1-, trh2-, and tdh2-lacZ fusion genes with or without mutations in the IRS. (A) Schematic representation of the promoter and IRS regions of the trh1, trh2, and tdh2 genes with or without mutations in the IRS that were fused to the lacZ gene. Two boxes, a circle, and large arrows (solid, open, or hatched) indicate the −35 and −10 regions of the promoter, the transcriptional start site, and the IRS, respectively. WT, wild-type sequence without mutation; M1, deletion of the IRS; M2 and M3, replacement of the IRS with the other IRS or corresponding tdh2 sequence. The long arrows indicate the location and the transcriptional direction of the lacZ gene, but the vector sequence is not shown. The designations of the pUJ8 derivatives or pUTminiTn5Sm/Sp derivatives containing the respective lacZ fusion constructs are indicated. β-Galactosidase activities of the E. coli MC1061 derivatives and V. parahaemolyticus AQ3815 derivatives carrying the plasmids indicated in panel A are shown in panels B and C, respectively. “None” indicates the parent strain without a lacZ fusion (a negative control). Each result represents the mean ± standard deviation determined from three or more randomly selected colonies.