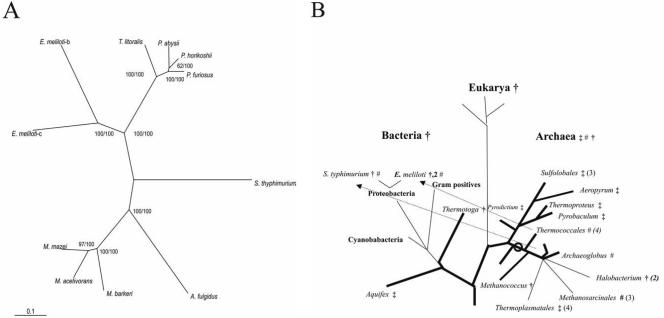
FIG. 5.
(A and B) Phylogenetic relationship of enzymes from the cPGI family (A) and distribution of PGIs in the universal phylogenetic tree (B). In panel A, the tree was constructed by the NJ algorithm of CLUSTAL X (50). The numbers at the nodes are bootstrapping values according to NJ (first) or ML (second). For NCBI accession numbers or SwissProt identifiers, see Fig. 4. In panel B, a phylogenetic tree according to 16S rRNA and 18S rRNA sequences (48) is shown. Organisms or groups of organisms are marked to contain PGIs belonging to the cPGI family (#) or to the PGI superfamily including the PGI family (†) and PGI/PMI family (‡). The proposed origin of the cPGI family in the euryarchaeal evolution is indicated by an open circle, and the postulated lateral gene transfers are indicated by arrows.