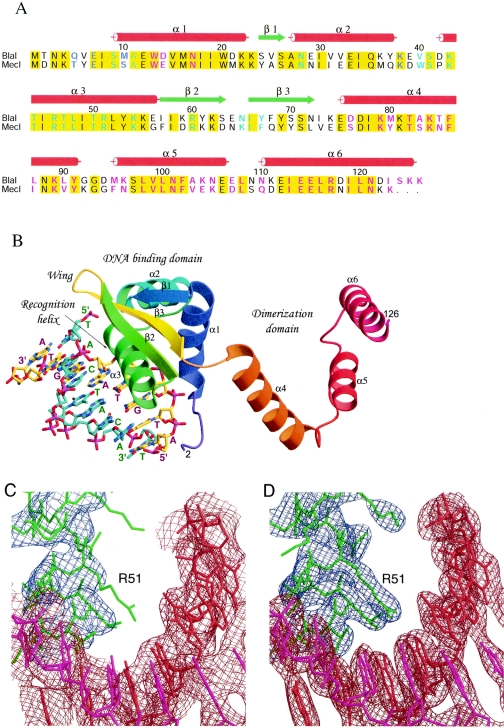
FIG. 2.
Sequence alignment, structure, and electron density maps of the BlaI-DNA complex. (A) Sequence alignment of BlaI and MecI repressor proteins. The proteins used in the alignment are as follows: BlaI, S. aureus N395 (Q9AC78), and MecI, S. aureus N395 (P26598). The red cylinders and green arrows indicate the secondary structural elements observed in the BlaI and BlaI-DNA crystals. Identical residues in the two sequences are shaded in yellow. Residues involved in DNA binding and dimerization are highlighted in cyan and magenta, respectively; those involved in both are in blue. (B) Overall structure of the BlaI monomer bound to DNA in the asymmetric unit. The protein molecule is shown as a ribbon representation, and the DNA is shown as sticks. The N-terminal domain has a winged helix topology that interacts with the TACA/TGTA motif of DNA via the recognition helix α3. Upon dimer formation, the three helices of the C-terminal domain intertwine with those from another monomer. (C) The refined model using the in-house data at 3.0-Å resolution is superimposed on the initial composite omit map based on the molecular replacement solution. The contour level is 1.0 σ centered about the residue Arg51. The model is shown as sticks in red and magenta for the double-stranded DNA and in green for the protein molecule. The DNA densities are shown in brown, and those for the protein are in blue. (D) The final model is superimposed on the 2Fo-Fc map calculated at 2.7-Å resolution from the synchrotron data set, contoured at a level of 1.5 σ.