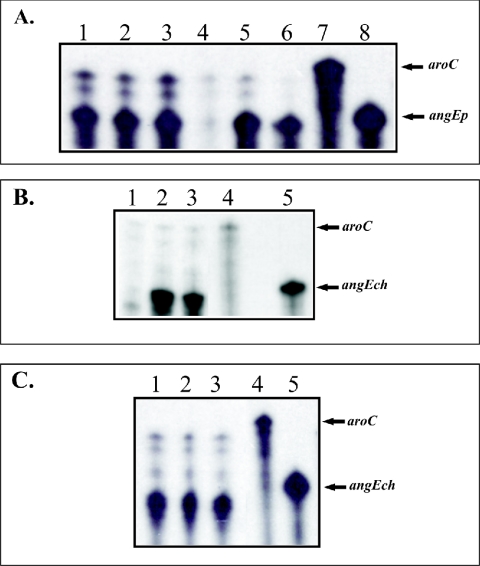
FIG. 3.
Transcriptional regulation analysis by RPA of the angEp and angEch genes. Total RNA was harvested from each strain grown under the conditions indicated for each lane. The riboprobes were synthesized using the Maxiscript T7/T3 kit from Ambion. In these experiments we used the aroC gene as an internal control because it was previously established that this gene is not regulated by iron (9). For aroC we used the plasmid pQSH6 (linearized with RsaI) (10, 15) and p32 for angEch gene. For the angEp homologue we designed the primers EPPU (5′ CCGATAGATATCATCACGAAA 3′) and EPPRT7 (5′ TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCGCGTAAAATCCGTTTTTATC 3′). The RPA assay was performed using the RPA III kit (Ambion) according to the manufacturer's specifications. Specific transcripts for aroC, angEch, and angEp were detected using the riboprobes synthesized as described above. (A) Analysis of the angEp gene. Lanes: 1, 2, and 3, RNA extracted from the V. anguillarum 775 MET 11 fur strain grown in CM9 supplemented with 4 μg of FAC, CM9, and CM9 supplemented with 2.5 μM EDDA/ml, respectively; 4, 5, and 6, RNA extracted from V. anguillarum strain 775 grown under the same conditions as described previously; 7, aroC riboprobe; 8, angEp riboprobe. (B) Analysis of the angEch gene. Lanes 1, 2, and 3: RNA extracted from V. anguillarum strain 775 grown in CM9 supplemented with 4 μg of FAC, CM9, and CM9 supplemented with 2.5 μM EDDA/ml, respectively. (C) Lanes 1, 2, and 3: same as described for panel B but using RNA from the V. anguillarum fur mutant strain. Lanes 4 and 5 of both panels show the aroC and angEch riboprobes.