Figure 1.
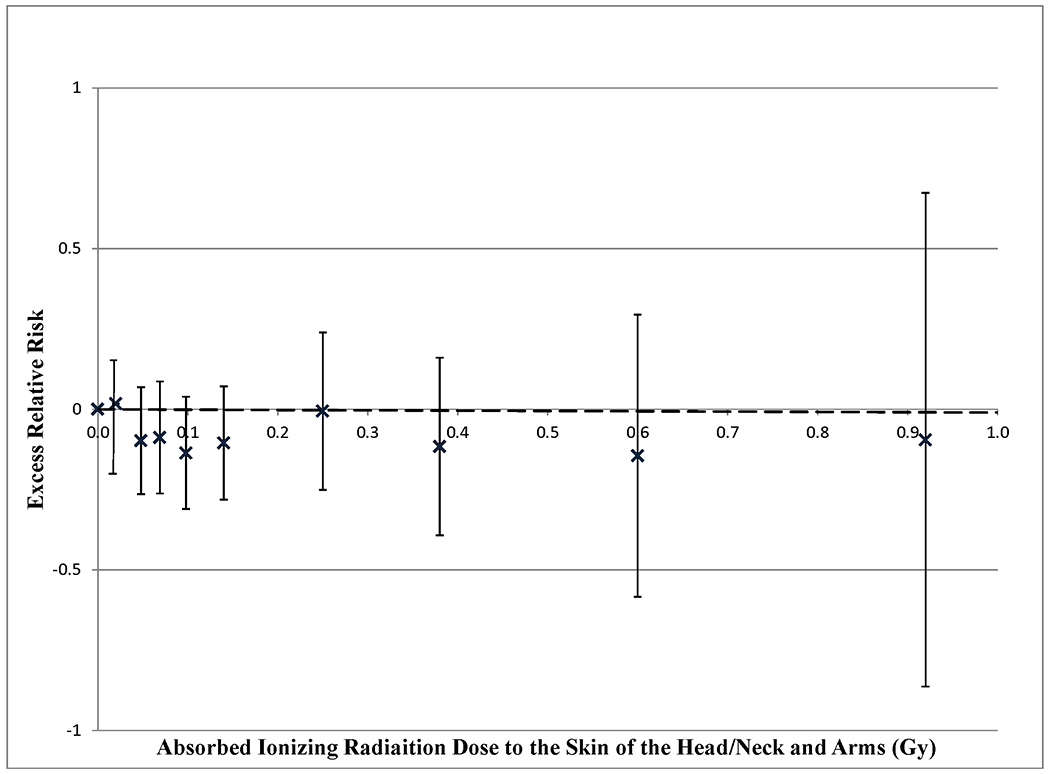
Excess relative risk of incident basal cell carcinoma by absorbed ionising radiation dose to the skin of the head, neck and arms in a cohort of U.S. radiologic technologists, 1983-2005, calculated using Poisson regression. Follow-up begins at the return of the first questionnaire (1983-1989) or second questionnaire (1994-1998) and ends at 31 December 2005. Calendar period adjustments are made by five calendar periods: 1983-84, 1985-89, 1990-94, 1995-99, 2000-05. Additional adjustments by sex (stratified), education, income, cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, body mass index, exercise, eye color, complexion, sun burn history, tanning sensitivity, dental x-rays and solar ultra violet exposure score. The dashed ( ) line represents a linear Poisson model using 12 age groups for attained age adjustment. Points with their respective confidence intervals use the same attained age adjustment ( X ). The ERRs are for radiation dose categories of : <10, 10-24, 25-49, 50-74, 75-99, 100-199, 200-299, 300-499, 500- mGy.
