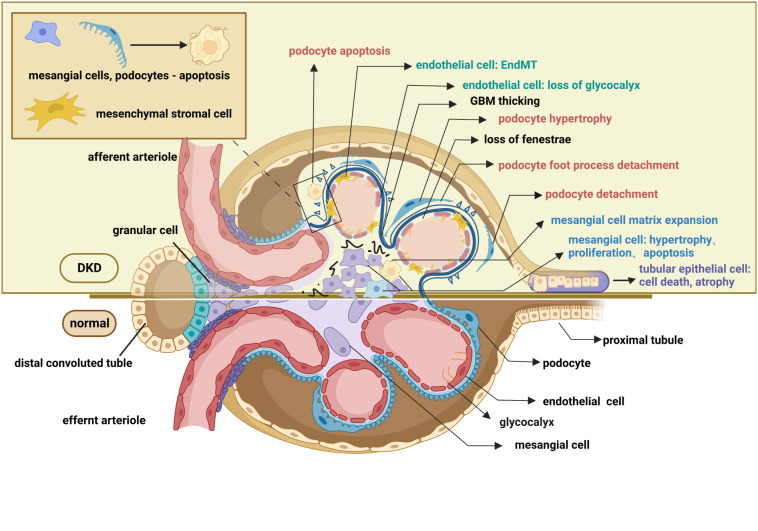
Figure 2.
Pathological changes in the glomerulus and renal tubule of DKD. The pathological changes of the glomerulus mainly involve glomerular endothelial cells, mesangial cells, glomerular basement membrane, and podocytes. Endothelial cell changes include loss of glycocalyx, endothelial-mesenchymal transformation, apoptosis, and pyroptosis. Changes in podocyte include podocyte apoptosis, podocyte hypertrophy, podocyte detachment, podocyte loss, and podocyte foot process effacement. Mesangial cell changes include proliferation, hypertrophy, and apoptosis. Pathological changes in the renal tubules include tubular epithelial cell apoptosis ferroptosis, pyroptosis, autophagy, epithelial-mesenchymal transformation, and peritubular pericyte migration. These lesions, as well as the thickening of the basement membrane and the accumulation of extracellular matrix, contribute to the exacerbation of fibrosis in diabetic kidneys. This figure is created with BioRender.com, and the authors have been granted a license to use the BioRender content.