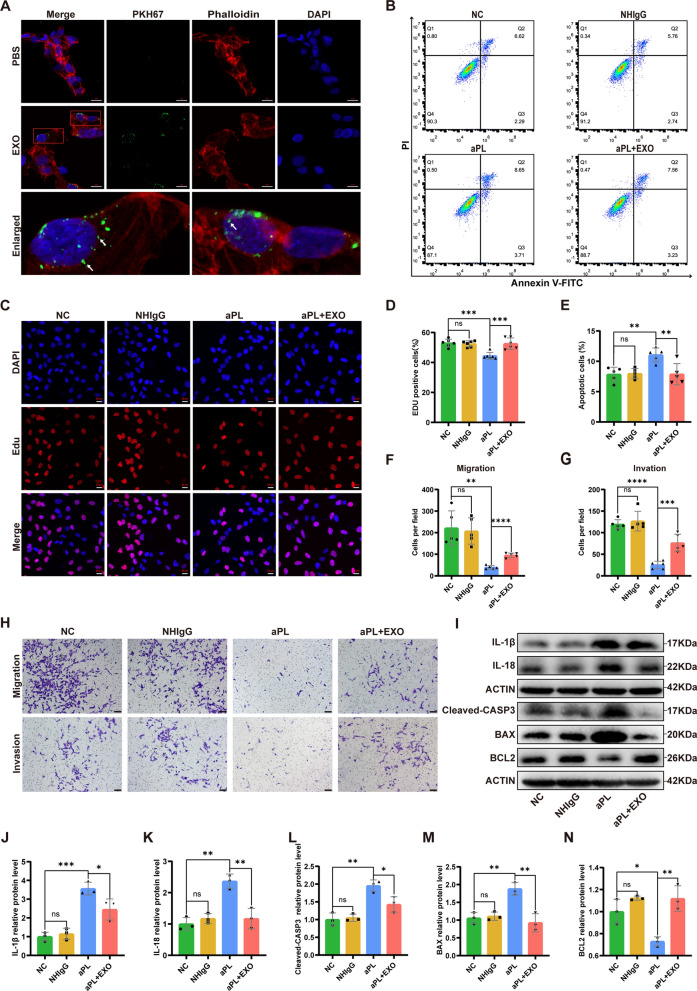
Fig. 2.
HucMSC-exos ameliorated the functional impairment of HTR8/SVneo cells caused by antiphospholipid antibody (aPL) in vitro. A Representative images of internalization of hucMSC-exos in HTR8/SVneo cells in vitro. Exosomes were labeled by PKH67, the cytoskeleton was stained with phalloidin-iFluor 594 and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 μm. B-N HTR8/SVneo cells were treated with NHIgG or aPL (200 μg/mL) for 24 h, and then hucMSC-exos were added into the medium (100 μg/mL) for 24 h. B and E The cell apoptotic rate was determined by flow cytometry analysis with annexin-V/PI staining (n = 5). C and D The proliferation ability of HTR8/SVneo cells in different treatment groups was detected by EdU assay (n = 6). Scale bars, 20 μm. F-H Transwell experiments were performed to measure the abilities of migration and invasion of HTR8/SVneo cells, hucMSC-exos improved the abilities of migration and invasion of HTR8/SVneo cells pretreated with aPL (n = 5). Scale bars, 100 μm. I-N Western blot analyzed the relative levels of apoptosis-related (Cleavd-CASP3, BAX, BCL2) and inflammation-associated (IL-1β, IL-18) proteins in HTR8/SVneo cells under different treatment conditions, quantified by signal intensity normalized to ACTIN (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001