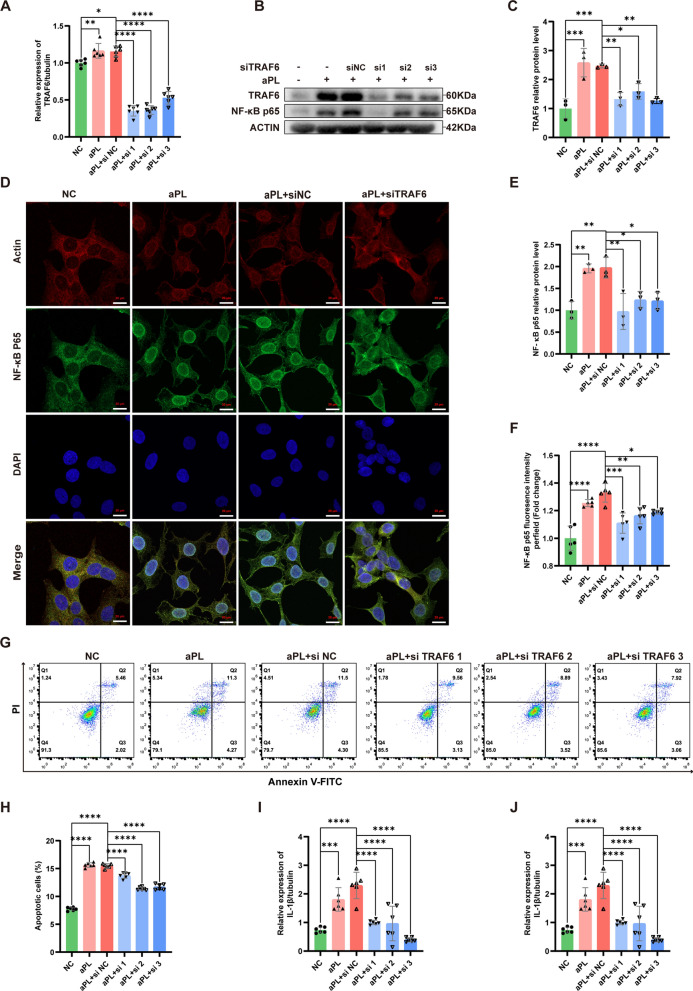
Fig. 6.
Knocking down of TRAF6 could inhibit the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 and attenuate the aPL-induced HTR8/SVneo cells injury. A The mRNA expression level of TRAF6 was detected by qRT-PCR in HTR8/SVneo cells infected with TRAF6 siRNA (n = 6). B, C and E The relative protein levels of TRAF6 and NF-κB p65 were detected by western blot in HTR8/SVneo cells infected with TRAF6 siRNA, quantified by signal intensity normalized to ACTIN (n = 3). D and F IF analyzed the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 in HTR8/SVneo cells infected with TRAF6 siRNA (NF-κB p65, green; Actin, red; DAPI nulcear stain, blue), (n = 5). Scale bars, 20 µm. G and H The cell apoptotic rate was determined by flow cytometry analysis with annexin-V/PI staining in HTR8/SVneo cells infected with TRAF6 siRNA (n = 5). I and J The mRNA expression levels of inflammatory cytokine factors (IL-1β and IL-18) in HTR8/SVneo cells infected with TRAF6 siRNA were examined by qRT-PCR assay (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001