Figure 5.
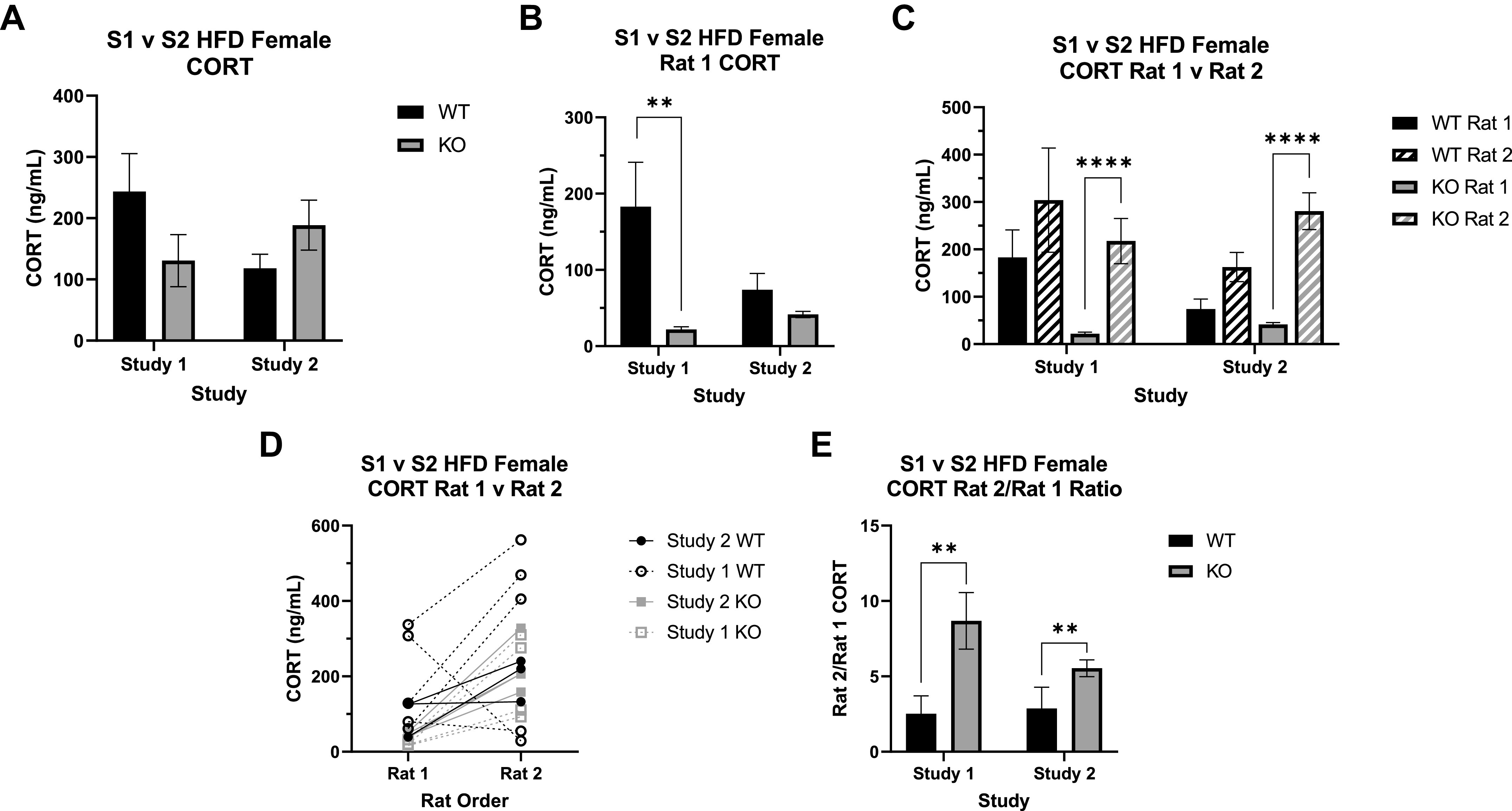
Corticosterone (CORT) measurements between study 1 (S1) and study 2 (S2) wild-type (WT) and Krtcap3 knockout (KO) rats. CORT was measured in the trunk blood collected at euthanasia. A: all rats evaluated together. When grouped only by study and genotype, there are no significant differences between WT (black) and KO (gray) CORT in either study 1 or study 2. Further assessment of the data revealed a third factor to consider, the order within the cage the rats were euthanized, either first (rat 1) or second (rat 2). Reanalysis with this additional variable revealed a significant interaction between study and genotype as well as one between genotype and order. HFD, high-fat diet. B: assessing only rats euthanized first. KO rats had lower CORT than WT rats in both studies, but this was statistically significant only in study 1, not study 2. **P < 0.01, effect of genotype respective to each study. C: comparing rats euthanized first and second. In both studies, KO CORT significantly increases in rat 2 of the cage, an effect that is not seen in the WT rats. ****P < 0.0001, effect of order respective to each genotype. D and E: rat 2/rat 1 CORT ratio (E). There was a significant main effect of genotype, where KO rats of both studies had a greater ratio than WT rats, indicating a greater CORT response. **P < 0.01, main effect of genotype.
