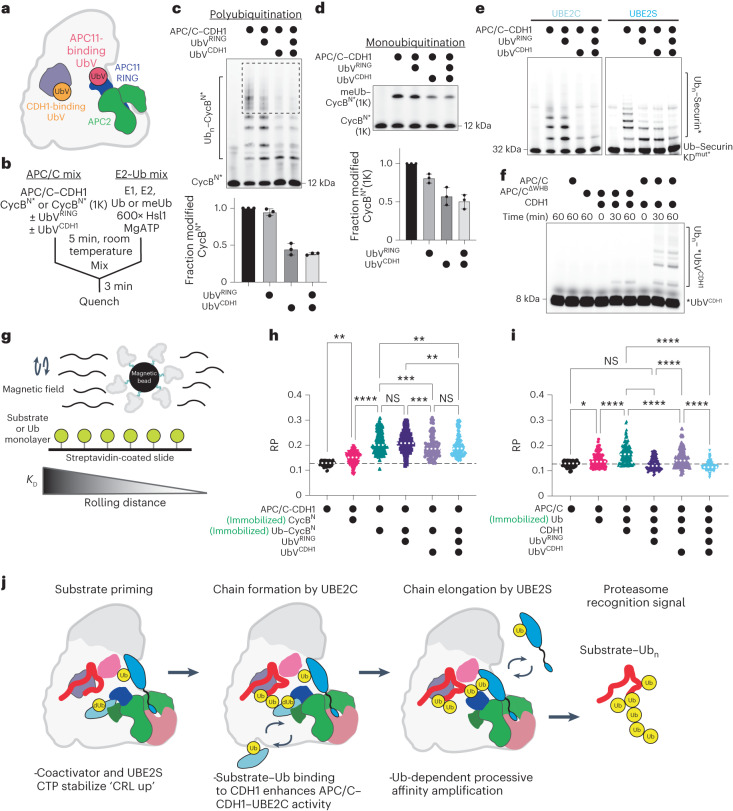
Fig. 5. Multiple Ub-binding sites promote processive ubiquitination by APC/CCDH1.
a, Cartoon model showing binding sites of CDH1-binding (UbVCDH1) and APC11-binding (UbVRING) UbVs. b, Workflow for single-encounter experiments. APC/CCDH1 and *CycBN containing multiple lysines or a single lysine (1K) are preincubated. The UbVs were added to this mixture. A second mix is prepared containing E1, UBE2C, MgATP, an excess of unlabeled Hsl1, and Ub or methylated Ub (meUb). The mixtures are combined, resulting in fluorescent substrate ubiquitination during a single binding event. c, Fluorescent scanning of an SDS–PAGE gel (top) and quantification (bottom) from single-encounter APC/C–CDH1–UBE2C-dependent polyubiquitination reactions with CycBN* and Ub. Dashed box indicates the region of CycBN* with >4 Ubs quantified in Extended Data Fig. 7a. n = 3 independent experiments. Error bars: standard error of the mean. d, Fluorescent scanning of an SDS–PAGE gel (top) and quantification (bottom) from single encounter of APC/C–CDH1–UBE2C-dependent substrate priming reactions with CycBN*(1K) and meUb. n = 3 independent experiments. Error bars: standard error of the mean. e, APC/C–CDH1-dependent ubiquitination reactions of Ub–Securin with its KEN- and D-box degrons mutated (Ub–Securin KDmut*) using either UBE2C (left) or UBE2S (right), monitored by fluorescent scanning. n = 3 independent experiments. f, Ubiquitination of fluorescently labeled *UbVCDH1 by APC/C–UBE2C is dependent on CDH1 and the APC2 WHB, monitored by fluorescent scanning. n = 3 independent experiments. g, METRIS setup to monitor binding of APC/C to a biotinylated substrate, Ub–substrate or Ub on a streptavidin-coated surface. Magnetic beads with biotinylated APC/C are subjected to a magnetic field. The movement of individual beads is quantitated to determine a rolling parameter (RP) that correlates with the strength of the interaction. h,i, Scatter plots quantitating the RP of the APC/C on surfaces containing CycBN or Ub-CycBN (h) or Ub (i) in the presence of UbVRING, UbVCDH1 or both. Experiments were compared using one-way analysis of variance (****P ≤ 0.0001, ***P ≤ 0.001, **P ≤ 0.005, *P ≤ 0.05). NS, not significant. j, Schematic of APC/C–CDH1–UBE2C–UBE2S-dependent substrate polyubiquitination. The APC/C catalytic architecture and recruitment of UBE2C~Ub (dUb) is influenced by CDH1 and UBE2S CTP binding to drive ubiquitination efficiency. Allosterically driven processivity of ubiquitination is further mediated by stabilizing contacts between multiple substrate-linked Ubs and CDH1 and APC11. Uncropped gels representative of n > 3 independent experiments for c–f available in source data.