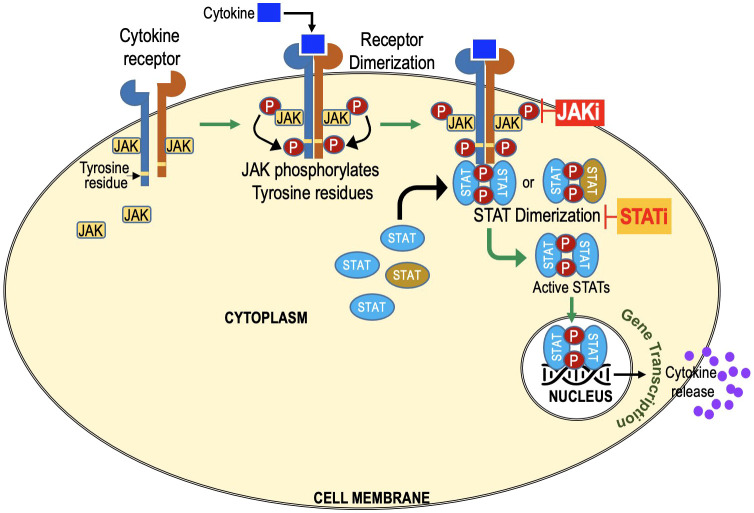
Figure 1.
JAK-STAT Signaling Cascade: Key Players in Cellular Regulation and Immune Responses. Extracellular molecules, such as cytokines or growth factors, bind to cell surface receptors, activating Janus Kinases (JAKs). Activated JAKs phosphorylate Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (STATs) at specific tyrosine residues, forming homo- or heterodimers in the cytoplasm. STAT dimers then translocate to the cell nucleus and act as transcription factors, regulating gene expression. JAK inhibitors target JAKs. STAT inhibitors target STATs and prevent dimerization and its translocation to nucleus.