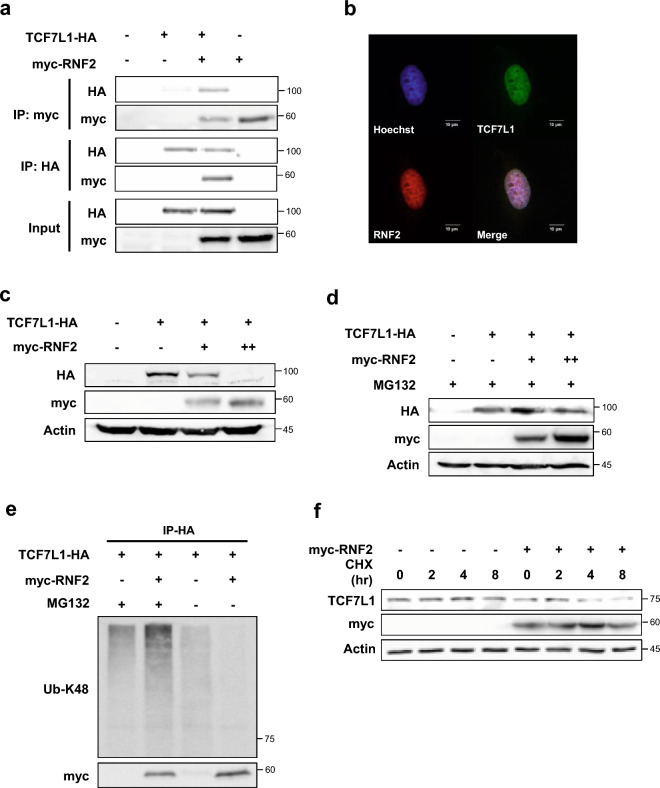
Figure 3.
RNF2 interacts with TCF7L1 and destabilizes TCF7L1. (a) Coimmunoprecipitation assay was performed using control HeLa cells. The indicated plasmids (6 μg TCF7L1-HA and 6 μg myc-RNF2) were transfected into cells, which were then treated with MG132 (10 μM, 12 h) and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-myc and anti-HA antibodies. (b) Immunocytochemistry assay was performed using control HeLa cells. Cells were fixed and stained with anti-TCF7L1 (green) and anti-RNF2 (red) after treatment with 10 μM MG132 for 12 h. Scale bar represents 10 μm. (c) Western blot analysis was performed using control HeLa cells. TCF7L1-HA (6 μg) and myc-RNF2 plasmids (3 μg and 6 μg) were introduced into cells, which were then lysed with RIPA buffer. (d) Western blot analysis was performed using control HeLa cells. TCF7L1-HA (6 μg) and myc-RNF2 plasmids (3 μg and 6 μg) were introduced into cells, followed by treatment with 10 μM MG132 for 12 h before harvest and lysed with RIPA buffer. (e) In vitro ubiquitination assay was performed using control HeLa cells. TCF7L1-HA (6 μg) and myc-RNF2 plasmids (6 μg) were introduced into cells, followed by treatment with 10 μM MG132 for 12 h before harvesting. The cells were lysed using the IP buffer and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA. Ubiquitination levels were determined by anti-UB-K48. (f) Cycloheximide chase assay was performed using control 4T1 cells. myc-RNF2 plasmids (6 μg) were introduced into cells, which were then treated with cycloheximide (10 μM) for 2, 4, and 8 h. Cells were lysed with RIPA buffer.