Fig. 8. Schematic diagram of this study.
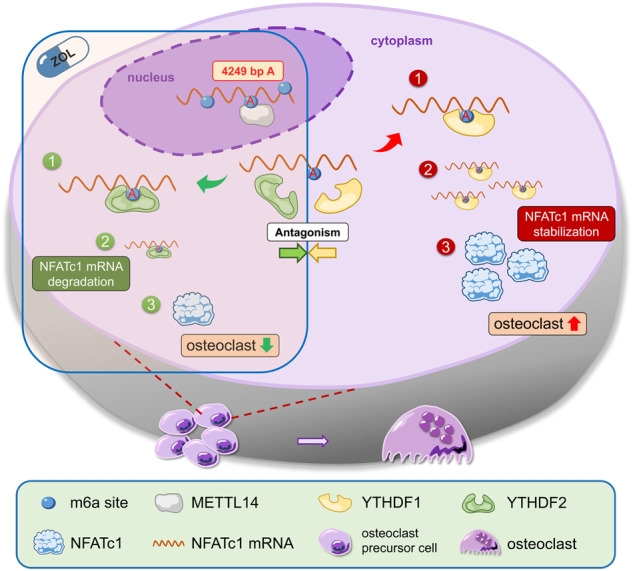
The increased level of NFATc1 m6A methylation caused by ZOL, in which 4249 A is the functional site, is highly correlated with the decreased function of bone resorption of osteoclasts. Upstream, METTL14 regulates osteoclast bone absorption through the methylation functional site of NFATc1. Downstream, YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 show competitive effects on the post-transcriptional regulation of NFATc1 after the m6A methylation level is elevated by METTL14.
