Figure 3.
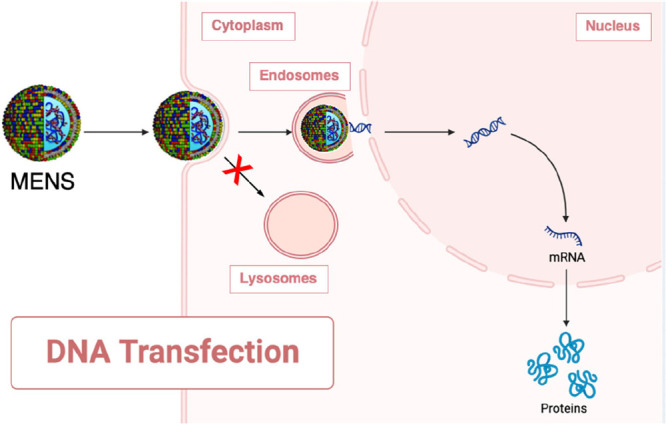
Schematic describing the performance of multicomponent envelope-type nanoparticle systems (MENS) as they navigate their way to the cell nucleus. Initially, MENS are internalized by the process of macropinocytosis, where they are taken up by the cell and enclosed within vesicles. Once inside the cell, MENS exhibit a unique characteristic: they diffuse freely within the cytosol. This diffusive behavior sets them apart from other nanoparticles and plays a crucial role in their overall performance. They possess the capability to maintain a low level of active transport, effectively avoiding pathways that would lead them to degrading lysosomes. This distinct feature allows MENS to preserve their integrity and functionality, ensuring that they remain intact throughout their journey within the cell. However, the true power of MENS lies in their exceptional DNA release from the endosomes. This process, likely due to gain in lipid mixing entropy,35 enables the DNA payload to escape the confines of the endosomes and gain access to the nucleus. The extensive nuclear entry achieved through effective DNA release is of paramount importance. It allows the DNA to reach its target destination within the cell, the nucleus, where it can exert its biological effects. The enhanced transfection efficiency resulting from successful nuclear entry is a key factor in the success of MENS as gene delivery systems. Cartoons were created using Biorender.com.
