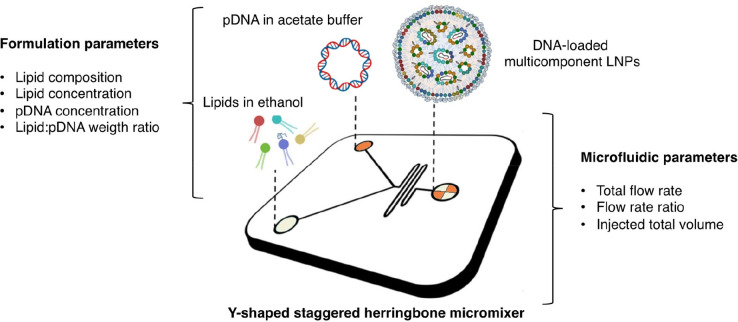
Figure 4.
Microfluidic manufacturing of multicomponent lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). The microfluidic manufacturing process of multicomponent LNPs loaded with plasmid DNA involves the utilization of a staggered herringbone micromixer (SHM). In this process, lipid blends dissolved in ethanol are injected through one inlet, while plasmid DNA dissolved in acetate buffer solution is injected through another inlet. At the Y-junction of the SHM, the two solutions converge and undergo chaotic mixing facilitated by the herringbone structure within the micromixer. This mixing phenomenon induces an increase in the polarity of the lipid solution, resulting in the formation of LNPs that encapsulate the plasmid DNA. Adjacent to the image, the text highlights two main categories of influential factors in the manufacturing process: synthesis and microfluidic parameters. Among these factors, lipid composition has been identified as a key parameter that governs the transfection behavior of both lipoplexes and multicomponent envelope-type nanoparticle systems (MENS). With this understanding, the hypothesis was put forth that the lipid composition of LNPs could modulate their ability to deliver the cargo when they interact and mix with cellular lipids. To explore this hypothesis, LNPs were prepared using the same lipid composition as that of MENS. Readapted with permission from ref (70). Copyright 2021 MDPI AG.