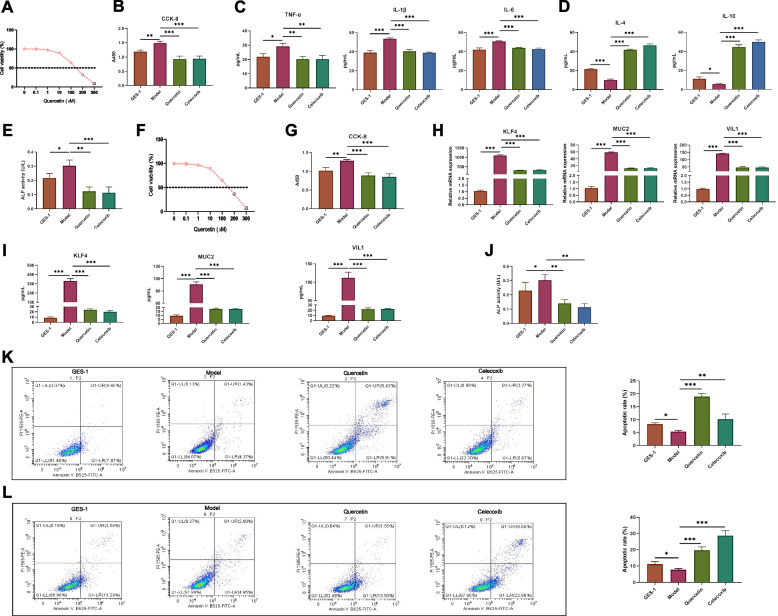
Fig. 9.
Quercetin inhibited inflammation and intestinal metaplasia levels in MNNG and CDCA-induced GES-1 cells. A IC50 of MNNG-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h. B Cell viability of MNNG-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h in CCK-8 assay. C TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 expression of MNNG-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h by ELISA. D IL-4 and IL-10 expression of MNNG-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h by ELISA. E ALP activity of MNNG-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h. F IC50 of CDCA-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h. G Cell viability of CDCA-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h in CCK-8 assay. H KLF4, MUC2, and VIL1 expression in CDCA-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h by qPCR. I MUC2, and VIL1 expression of CDCA-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h by ELISA. J ALP activity of CDCA-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24h. Apoptosis of (K) MNNG-GES-1 and (L) CDCA-GES-1 cells after quercetin treatment for 24 h by flow cytometry. The mean ± standard deviation was used to express all data, and there were at least three samples in each group. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) methods were performed for comparisons between groups. P-values < 0.05 denoted statistically significant differences. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001