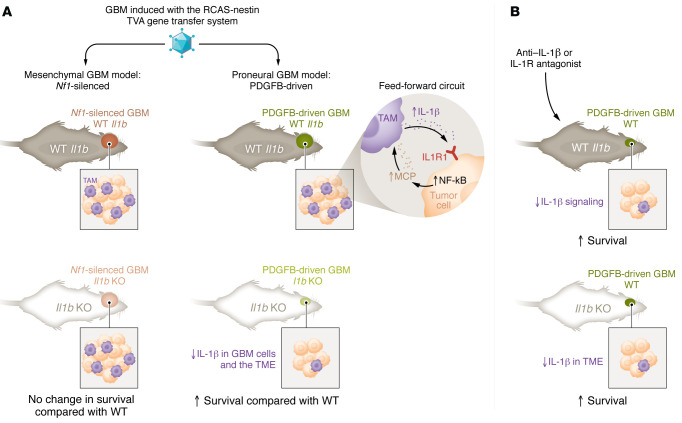
Figure 1. PDGFB-driven GBM cells and TAMs that express IL-1β establish a feed-forward loop.
(A) Chen, Giotti, et al. determined that the requirement for IL-1β in GBM growth differed based on tumor cell genotype. The RCAS/Ntv-a system was used to drive GBMs based on elevated PDGFB expression or Nf1 knockdown in a genetic background with or without IL-1β knockout. Survival of mice with PDGFB-driven but not Nf1-silenced GBMs was increased in Il1b-knockout mice. In PDGFB-driven GBMs, IL-1β stimulated NF-κB activity and MCP production to increase BMDM infiltration. In contrast, high basal levels of NF-kB activity in Nf1-silenced GBMs drove growth via MCP production and BMDM infiltration. (B) IL-1β specifically from the TME drives tumor growth. Targeting of IL-1β or its receptor IL1R1 improved the survival of mice bearing PDGFB-driven GBMs. Similarly, Il1b loss in the TME, but not GBM, cells limited GBM growth and increased survival in mice.