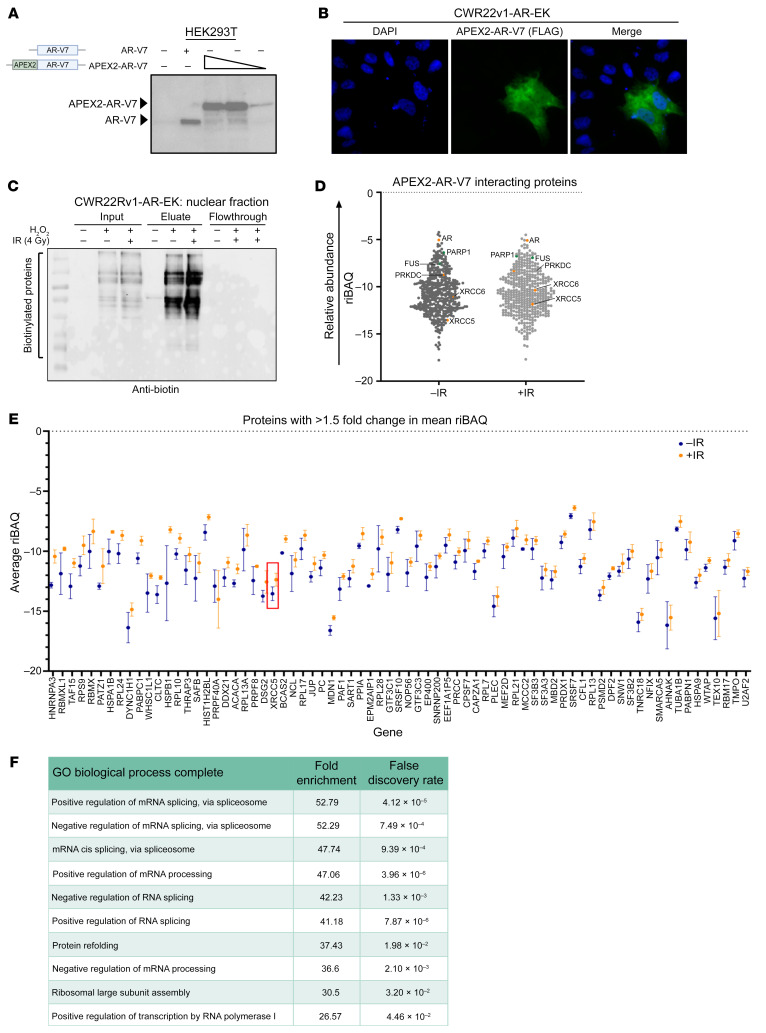
Figure 1. AR-V7 proximal biotinylation experiments identify known AR-V7 interactors and the DNA-PKcs holoenzyme.
(A) Diagrammatic representation of APEX2-AR-V7 construct and anti-AR Western blot of HEK293T cells transiently transfected with either AR-V7 or increasing quantities of FLAG-APEX2-AR-V7 constructs. (B) 1 × 105 CWR22Rv1-AR-EK cells were transfected with 2 μg of a FLAG-tagged APEX2-AR-V7 construct for 48 hours and again for an additional 24 hours prior to immunofluorescence using an anti-FLAG antibody. Magnification ×40. (C) 5 × 106 CWR22Rv1-AR-EK cells were transfected with 10 μg pLV-FLAG-APEX2-AR-V7 and again 48 hours later prior to treatment with biotin-phenol and with or without IR (4 Gy) for 2 hours. In the –IR and +IR arms, H2O2 was added to cells to induce the labeling reaction. Cells were then quenched and harvested, and the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were isolated and quantified. 10 μg resultant nuclear lysate was analyzed by Western blotting using an HRP-linked anti-biotin antibody. Corresponding Ponceau Red stain is shown to indicate equal sample loading. (D) Plot of mean riBAQ scores of all APEX2-AR-V7–interacting proteins identified by mass spectrometry. AR and components of the DNA-PK holoenzyme are highlighted in orange, and two known AR interactors, PARP1 and FUS, are highlighted in green. (E) APEX2-AR-V7–interacting proteins that have a riBAQ score >1.5-fold in response to irradiation. Ku80 (XRCC5) is highlighted in a red box. Data points represent the mean of 2–3 replicates (depending on if the protein is identified in 2 or 3 replicates) ± SEM. (F) Top 10 biological processes that are enriched in the list of proteins that are more abundant AR-V7 interactors in response to irradiation.