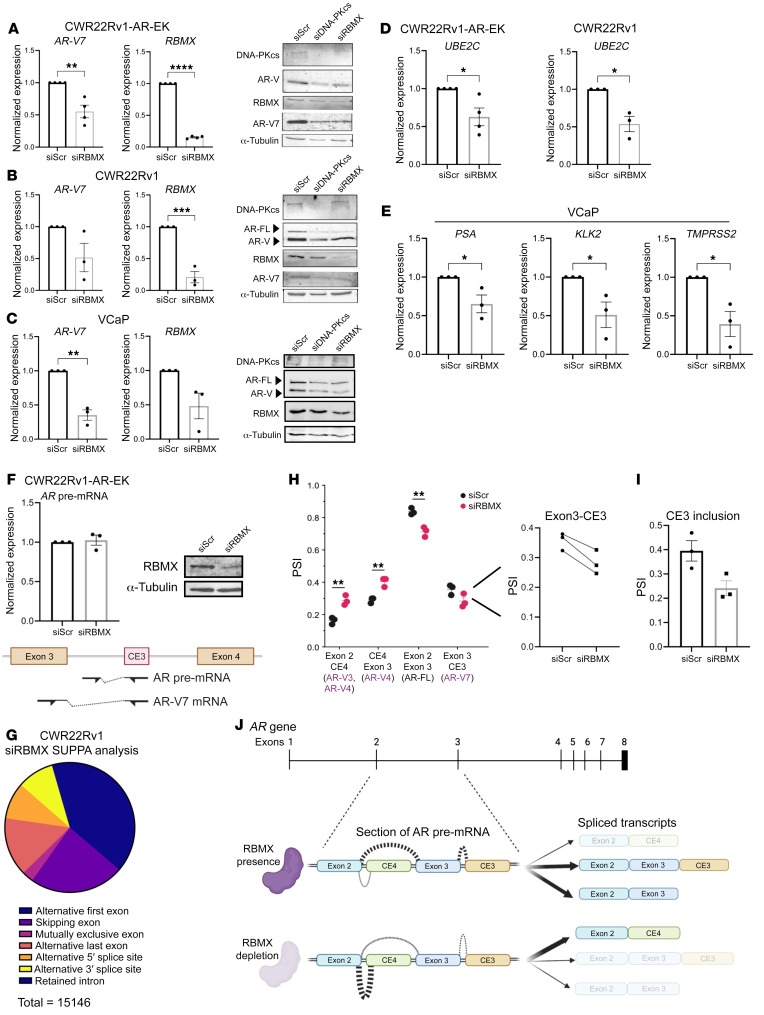
Figure 7. RBMX regulates AR-V synthesis in prostate cancer.
(A) CWR22Rv1-AR-EK, (B) CWR22Rv1, and (C) VCaP cells grown in serum-containing and steroid-depleted media, respectively, were transfected with RBMX (siRBMX) or scrambled control (siScr) siRNAs for 72 hours prior to AR-V7 and RBMX transcript analysis using RT-qPCR. Data represent the mean of 3 repeats ± SEM. An unpaired 2-tailed t test was used to determine the statistical significance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. In parallel, AR, AR-V7, DNA-PKcs, and RBMX protein levels were analyzed by Western blot in cells depleted of DNA-PKcs and RBMX for 72 hours. (D) CWR22Rv1-AR-EK and CWR22Rv1 and (E) VCaP cells were depleted of RBMX, as in A–C, and canonical AR-V–target gene expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Data represent the mean of 3 repeats ± SEM. An unpaired 2-tailed t test was used to determine the statistical significance. *P < 0.05. (F) CWR22Rv1-AR-EK cells depleted of RBMX for 72 hours were subject to qRT-PCR analysis to assess unspliced, pre-mRNA AR transcript abundance compared with scrambled siRNA (siScr) control. Representative Western analysis is shown to demonstrate successful RBMX knockdown. (G) RNA-Seq data derived from CWR22Rv1 cells depleted of RBMX was analyzed for differential splicing activity using SUPPA2. Events that passed a P value cut off of < 0.05 were plotted in the pie chart. (H and I) Altered exon composition of distinct AR transcripts as calculated by investigating relative exon inclusion (PSI) for all junctions measured using (H) hisat2 and (I) SUPPA2. (J) Diagrammatic representation of exon inclusion dynamics across exon 2 to cryptic exon 3 (CE3) in steady-state and in response to RBMX knockdown.