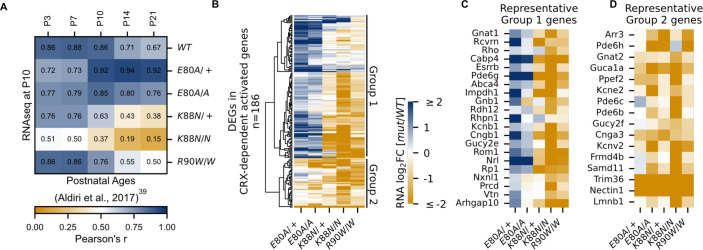
Figure 3. CRX-dependent activated genes affected in opposite directions in developing CrxE80A and CrxK88N mutant retinas.
(A) Heatmap showing sample-wise Pearson correlations of the expression of all CRX-dependent activated genes between P10 wild-type (WT) and homeodomain (HD) mutant mouse retinas in this study (rows) with postnatal WT retinas from age P3 to P21 (columns, data from GSE87064). (B) Heatmap showing the expression changes of DEGs in CRX-dependent activated gene set in HD mutant mouse retinas at P10. (C, D) Heatmaps showing expression changes of selected photoreceptor genes from Groups 1 and 2. Color scale identical to (B).