Figure 1.
DOT1L is loss of function constrained and conserved in flies
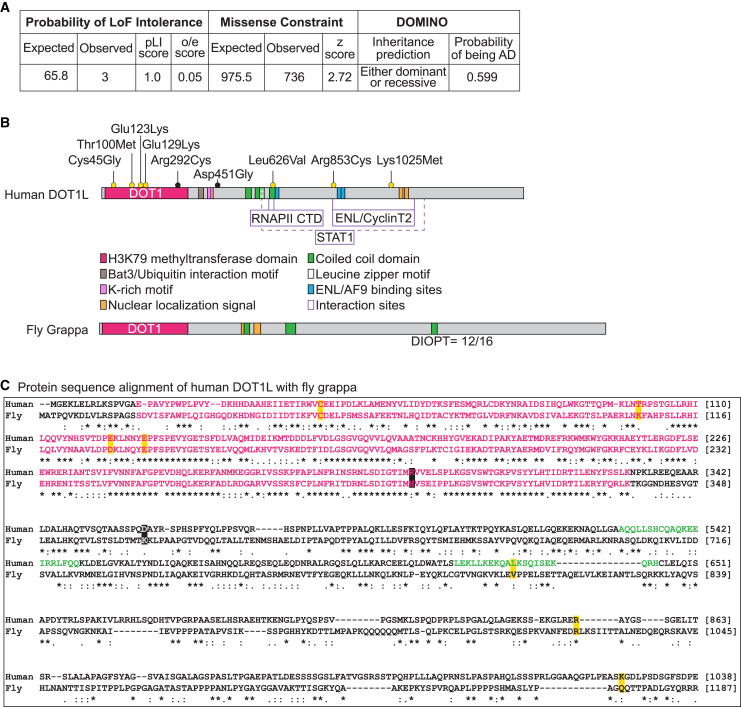
(A) DOT1L is variant constrained based upon the control population database, gnomAD.51 Variants in DOT1L are predicted to be inherited “either recessive or dominant” and have a score of 0.599 for “probability of being autosomal dominant” by DOMINO.
(B) Protein domain organization of human DOT1L and its fly (gpp) ortholog. Domains of DOT1L and the region they span specified with amino acid numbers are as follows: catalytic domain DOT1 (16–330),9,10 Bat3/Ubiquitin interaction motif (361–380),17 K-rich motif (390–407)9 with a partially overlapping nuclear localization signal (NLS) (395–417),52 three coiled-coil domains (529–549, 564–595, 616–636),53 leucine zipper motif (576–594),54 CTD binding patch (618–627),25 three ENL/AF9 binding sites (628–653, 863–878, 877–900),55,56,57 two more NLSs (1,088–1,111 and 1,164–1,171),52 and STAT1 interaction region (580–1,138).58 Variants suspected to be diagnostic are indicated above the protein as yellow dots and the variants suspected to be non-diagnostic are indicated as black dots. DOT1L’s ortholog in fly, gpp, has a DOT1 domain, three coiled-coil domains, and two NLSs. Gpp has a homology score 12/16 (DIOPT, v.8.5).59
(C) Protein sequence alignment of human DOT1L (Uniprot: Q8TEK3) and fly gpp (UniProt: Q8INR6). The variants are highlighted with yellow or black boxes. Pink letters correspond to the DOT1 domain and green letters correspond to a coiled-coil domain. Symbols in the protein alignment: fully conserved (∗), strongly similar (:), weakly similar (.), absent (−).