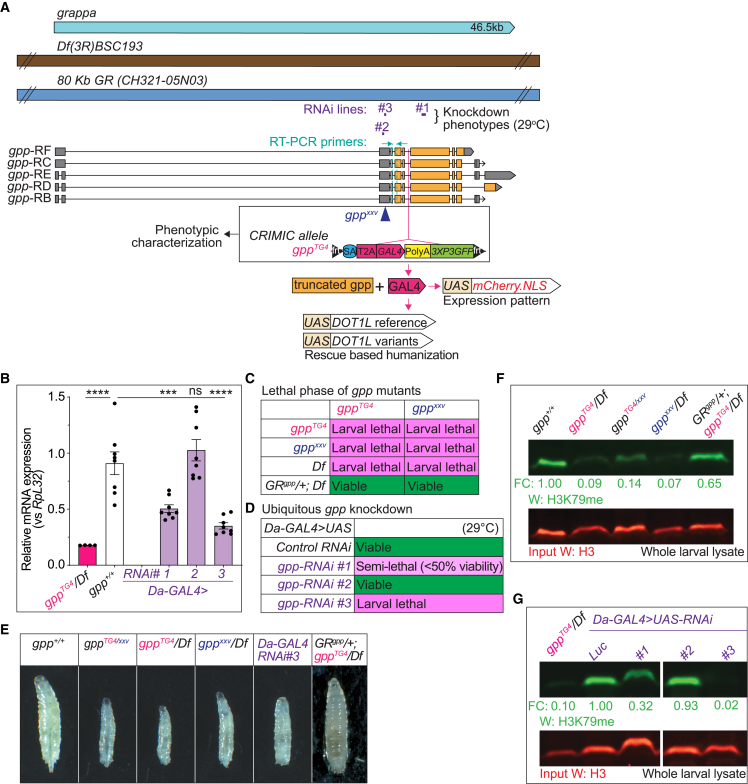
Figure 2.
Fly grappa is essential for development and loss of gpp leads to developmental delay and a reduction in H3K79 methylation
(A) Gene structure of fly gpp, fly reagents, and assays used in this study. The gene region is shown in light blue. A deficiency and genomic rescue (GR) construct are shown in brown and dark blue, respectively. Three independent RNAi lines (#1, P{TRiP.JF01284}attP2; #2, P{TRiP.GL01325}attP2; and #3, P{TRiP.HMJ02129}attP40) tested in this study and their target regions are shown in purple. Different isoforms of gpp (RB, RC, RD, RE, and RF) are shown in the middle panel and exons are indicated in orange, introns as black lines, and untranslated regions (UTR) in gray. gpp mutants used in phenotypic characterization studies include gppxxv (X-ray mutagenesis)28 and gppTG4 (CRIMIC allele).
(B) Relative gpp mRNA expression levels are lower than 20% in gppTG4/Df mutant larvae when compared to controls (gpp+/+) based on real-time qPCR using primers shown in (A). Real-time qPCR analysis of gpp mRNA levels in ubiquitous gpp knockdown larvae shows that Da-GAL4 > gpp-RNAi reduces gpp expression to different levels. Da-GAL4 > gpp-RNAi #1 decreases gpp mRNA levels by ∼50% and RNAi #3 by 70%. RNAi #2 does not have any effect on gpp levels. Normalized gpp levels from three independent experiments were plotted as mean ± SEM, and statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA for multiple groups (∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).
(C) Animals homozygous for gpp mutant alleles are larval lethal. None of the alleles or a large deficiency allele which lacks gpp, Df(3R)BSC193, can complement each other. One copy of a genomic rescue construct inserted in second chromosome (VK37), GRgpp/+, rescues lethality of trans-heterozygous allelic combinations.
(D) Ubiquitous knockdown of gpp results in larval lethality. While Da-GAL4 > RNAi #3 flies are larval lethal, -RNAi #1 flies are semi-lethal, as shown by lower-than-expected genotypic ratios of survival into adulthood. RNAi #2 flies are completely viable. Da-GAL4 > UAS-gpp-RNAi flies were compared to Da-GAL4 > control-RNAi (control-RNAi = UAS-luciferase-RNAi). All the crosses were performed at 29°C.
(E) Complete loss or ubiquitous knockdown (<50%) of gpp leads to severe developmental delay. Images of age-matched larvae at third instar larval stage is shown. One copy of a genomic rescue construct inserted in second chromosome (VK37), GRgpp/+, can rescue the developmental delay phenotype.
(F) Gpp mutant animals have a drastic decrease in H3K79 methylation levels. Protein lysate from 10 larvae was prepared for each sample. H3K79 methylation levels were normalized with loading control, H3, and fold change (FC) for each sample were calculated by comparing normalized H3K79 methylation levels to wild-type larvae (gpp+/+). One copy of the genomic rescue construct, GRgpp/+, can increase the H3K79 methylation levels to ∼65%.
(G) Ubiquitous knockdown (<50%) of gpp causes a severe decrease in H3K79 methylation levels. Da-GAL4 > gpp-RNAi #1 decreases H3K79 methylation levels to ∼30% and RNAi #3 to ∼2%. RNAi #2 does not have any effect on methylation levels. Protein lysate from 10 larvae was prepared for each sample. H3K79 methylation levels were normalized with loading control, H3, and FC for each sample were calculated by comparing normalized H3K79 methylation levels to control-RNAi (control-RNAi = UAS-luciferase-RNAi). All the crosses were performed at 29°C. A sample which is excluded from this study is cropped out from the gel image.