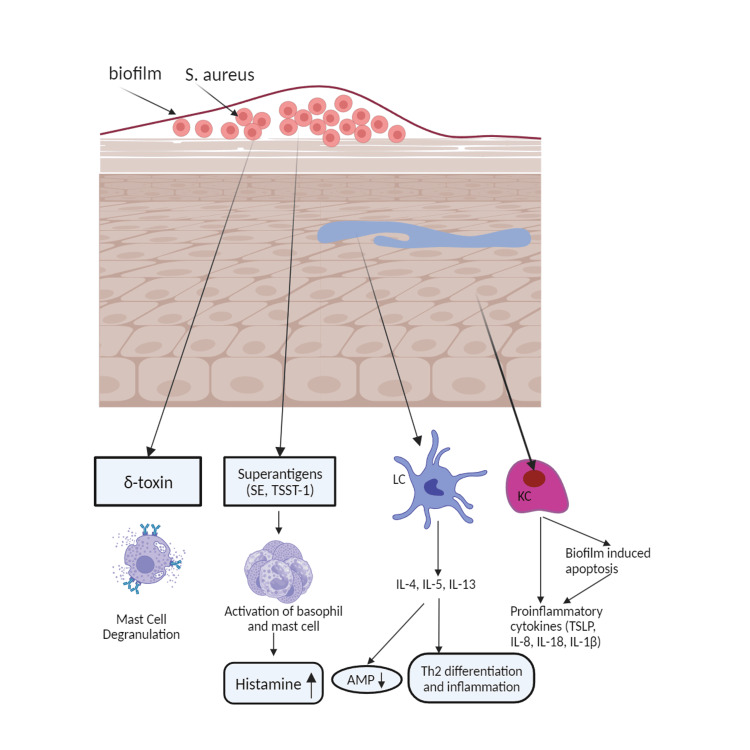
Figure 5. Atopic dermatitis can be caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Staphylococcus aureus produces superantigens like staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1), activating basophils and mast cells and releasing histamine. Langerhans cell (LC) is activated, releasing interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-5 (IL-5), and interleukin-13 (IL-13), causing antimicrobial peptides (AMP) reduction, T-helper2 differentiation, and inflammation. Keratinocyte (KC) is stimulated, releasing proinflammatory cytokines like thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), interleukin-8 (IL-8), interleukin (IL-18), and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). Biofilm induces keratinocyte (KC) apoptosis, releasing inflammatory cytokines. S. aureus can also release delta toxin (δ-toxin), causing mast cell degranulation.
This figure was created by AA, one of the authors of this article with Biorender.com.