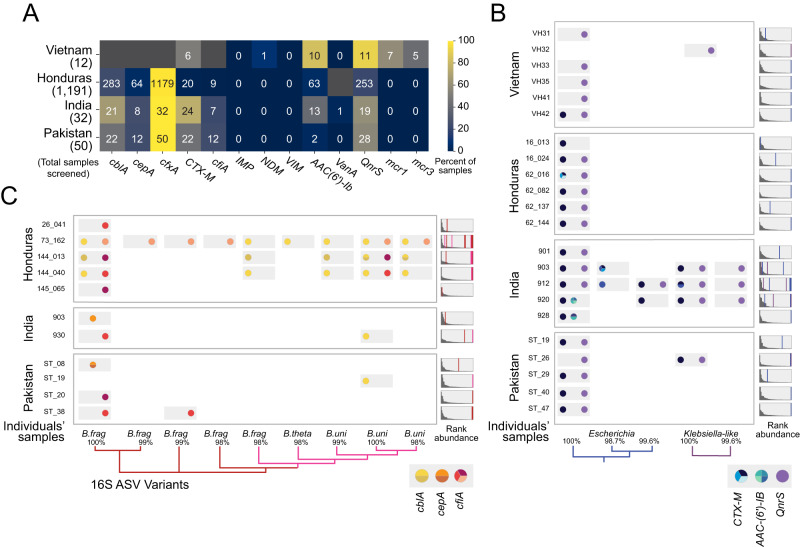
Fig. 3. OIL-PCR confirms that select AR genes are taxonomically restricted.
A A heatmap showing the number and percentage of gut microbiome samples that were positively screened for each AR gene, by quantitative PCR (for Vietnam, India and Pakistan) or metagenomic read alignment (Honduras). Bolded AR genes were further screened for taxonomic associations by OIL-PCR. Dark gray boxes indicate qPCR reactions that were not performed. B OIL-PCR was performed to detect taxonomic associations for CTX-M, AAC-(6’)-IB, and qnrS in positive gut microbiome samples from the international cohorts. Each row represents an individual’s gut microbiome sample. Colors represent AR gene variants. Phylogenies show the relationships between detected ASVs. The percent similarity is listed. To the right of each sample is a rank-ordered distribution of abundances of the individual ASVs in the individual’s gut microbiome, as determined by 16 S rRNA sequencing. Lines, colored according to the species designated in the phylogenies, are placed at the rank of the ASVs detected by OIL-PCR in each sample. C OIL-PCR results performed in cfiA, cblA, and cepA, displayed in the same manner as in (B). 31 individuals’ samples are shown in (B) and (C), with two individuals having been tested for the genes in both (B) and (C).