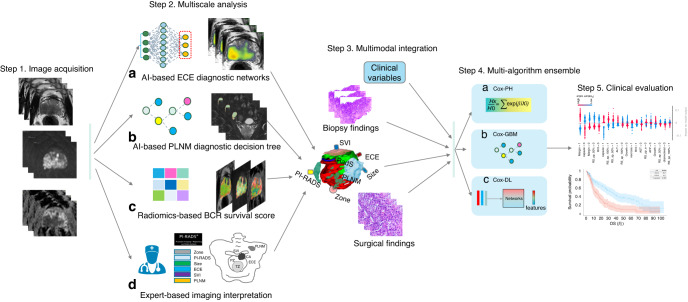
Fig. 1. Flowchart of iBCR-Net construction.
The study consists of the following primary steps: first, individual prostate MRI within the cohort of study, in response to each pathological status, is acquired by a panel of experts and is evaluated with a pretrained AI-based network for diagnosing ECE (a) and a pretrained diagnostic model for PLNM (b), respectively. Tumour radiomics features are extracted on T2WI, b1500 DWI and ADC images and processed with a Lasso-Cox regression algorithm to derive a radiomics survival (RadS) score that connects to BCR survival outcome (c). Additionally, expert-based interpretation for PI-RADS score, tumour size, tumour zone, T stage and N stage, etc., is done by the panel of radiologists (d). Then, the newly determined imaging biomarkers, together with clinicopathologic variables, are fed into a stack of Cox-based algorithms, including Cox-PH, Cox-GBM and Cox-DL, to derive a prognostic model for BCR survival outcome. Last, the model is validated clinically in independent test data. ECE extracapsular extension, PLNM pelvic lymph node metastasis, BCR biochemical recurrence, SVI seminal vesicle invasion, Cox-PH Cox proportional hazards, Cox-GBM Cox gradient boosting machine, Cox-DL deep learning-based Cox model.