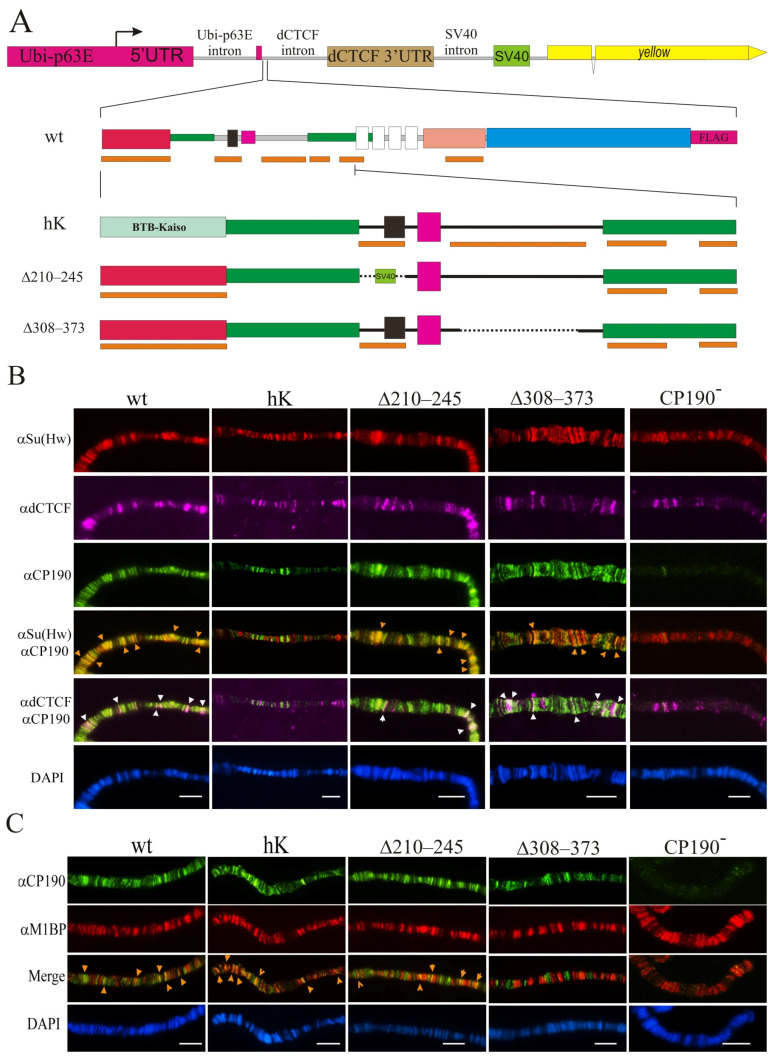
Figure 2.
Binding of the CP190 variants to polytene chromosomes. (A) Schematic representation of the CP190 variants. The expression vector is shown above: the Ubi-p63E promoter with its 5′UTR and 3′UTR from the dCTCF gene fused with the SV40 region including polyadenylation signals. The intronless yellow gene (not to scale) was used as a reporter. Below are shown the full-length schemes of the CP190WT-F coding region and the N-terminal regions of the CP190hK–F, CP190Δ210–245–F, and CP190Δ309–390–F derivatives. Other designations are as in Figure 1. Cytological localization (B) of CP190, dCTCF, and Su(Hw) and (C) CP190 and M1BP proteins on the polytene chromosomes of the Ubi:CP190*/CyO; Cp1902/Cp1903 lines, where Ubi:CP190* is either Ubi:CP190WT(WT), Ubi:CP190hK(hK), Ubi: CP190Δ210–245(Δ210–245), or Ubi:CP190Δ309–373(Δ309–373). CP190− represents the Cp1902/Cp1903 mutant line. The panels show the immunostaining using (B) anti-Su(Hw) (red), mouse anti-dCTCF (magenta), and rat anti-CP190 (green) antibodies, and (C) the rat anti-CP190 (green) and rabbit anti-M1BP (red) antibodies. Arrows indicate sites of protein colocalization. DAPI staining of polytene chromosome squashes is represented in blue. Scale bars, 10 μm.