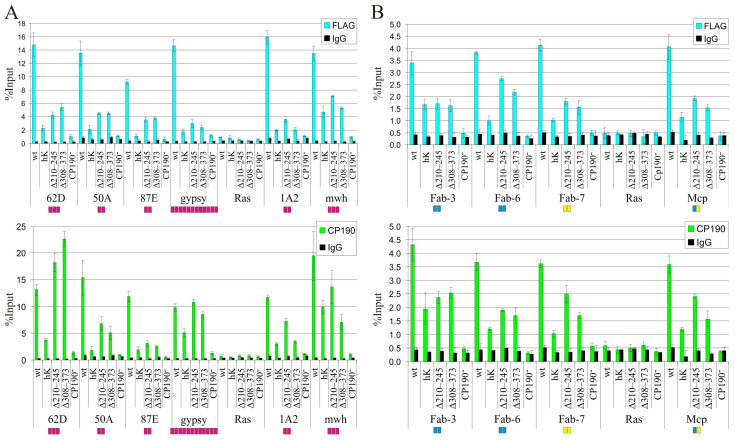
Figure 3.
The results of experiments designed to evaluate the ability of the CP190 variants to bind the selected chromatin sites. ChIP-qPCR analysis of CP190 binding to chromatin was performed using third-instar larvae of transgenic lines expressing different variants of the CP190 protein: CP190WT-F (wt), CP190hK–F (hK), CP190Δ210–245–F (Δ210–245), CP190Δ309–373–F (Δ309–373), and control Cp1902/Cp1903 (Cp190−). The most well-characterized CP190-bound sites associated with different architectural proteins were studied: (A) Su(Hw) binding regions. Magenta squares indicate the number of Su(Hw) binding sites in the tested regions. (B) Boundaries in the Bithorax complex. Blue squares indicate the number of dCTCF binding sites, and yellow squares indicate the number of Pita binding sites in the tested regions. Immunoprecipitation was performed with either FLAG (blue bars) or CP190 (green bars) antibodies. PCR products were amplified from three separate immunoprecipitates of three different chromatin preparations. The ras64B coding region (Ras) was used as a control, being devoid of CP190 binding regions. The percentage recovery of immunoprecipitated DNA (Y axis) was calculated relative to the amount of input DNA. Error bars indicate standard deviations of three independent biological replicates.