Abstract
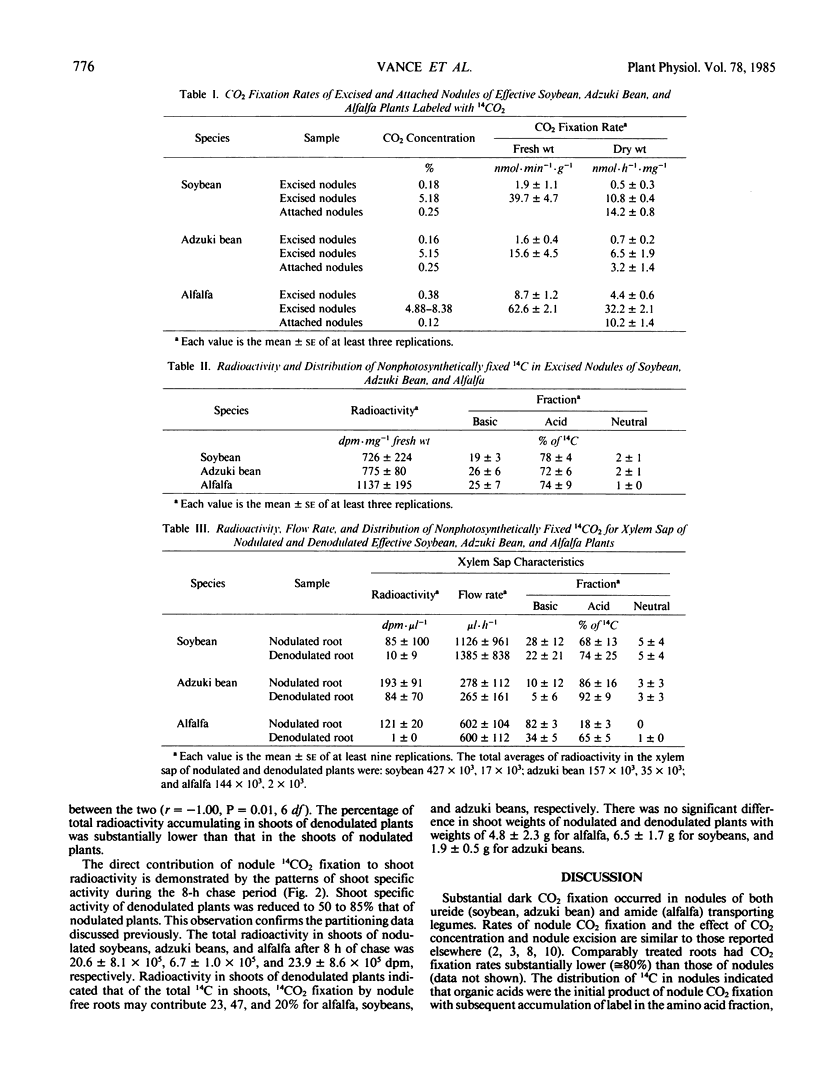
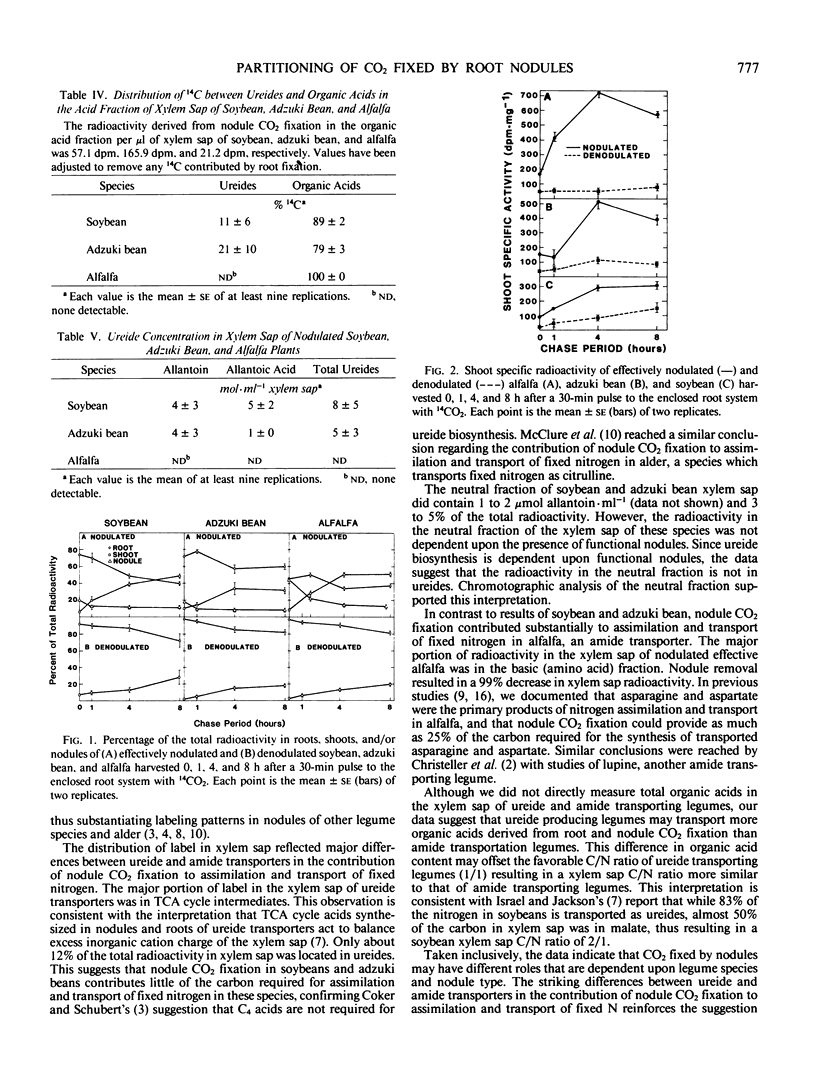
Nodulated and denodulated roots of adzuki bean (Vigna angularis), soybean (Glycine max), and alfalfa (Medicago sativa) were exposed to 14CO2 to investigate the contribution of nodule CO2 fixation to assimilation and transport of fixed nitrogen. The distribution of radioactivity in xylem sap and partitioning of carbon fixed by nodules to the whole plant were measured. Radioactivity in the xylem sap of nodulated soybean and adzuki bean was located primarily (70 to 87%) in the acid fraction while the basic (amino acid) fraction contained 10 to 22%. In contrast, radioactivity in the xylem sap of nodulated alfalfa was primarily in amino acids with about 20% in organic acids. Total ureide concentration was 8.1, 4.7, and 0.0 micromoles per milliliter xylem sap for soybean, adzuki bean, and alfalfa, respectively. While the major nitrogen transport products in soybeans and adzuki beans are ureides, this class of metabolites contained less than 20% of the total radioactivity. When nodules of plants were removed, radioactivity in xylem sap decreased by 90% or more. Pulse-chase experiments indicated that CO2 fixed by nodules was rapidly transported to shoots and incorporated into acid stable constituents. The data are consistent with a role for nodule CO2 fixation providing carbon for the assimilation and transport of fixed nitrogen in amide-based legumes. In contrast, CO2 fixation by nodules of ureide transporting legumes appears to contribute little to assimilation and transport of fixed nitrogen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christeller J. T., Laing W. A., Sutton W. D. Carbon Dioxide Fixation by Lupin Root Nodules: I. Characterization, Association with Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase, and Correlation with Nitrogen Fixation during Nodule Development. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):47–50. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coker G. T., Schubert K. R. Carbon Dioxide Fixation in Soybean Roots and Nodules: I. CHARACTERIZATION AND COMPARISON WITH N(2) FIXATION AND COMPOSITION OF XYLEM EXUDATE DURING EARLY NODULE DEVELOPMENT. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):691–696. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herridge D. F., Atkins C. A., Pate J. S., Rainbird R. M. Allantoin and Allantoic Acid in the Nitrogen Economy of the Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp.). Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):495–498. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. W., Jackson W. A. Ion balance, uptake, and transport processes in n(2)-fixing and nitrate- and urea-dependent soybean plants. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jan;69(1):171–178. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure P. R., Coker G. T., Schubert K. R. Carbon Dioxide Fixation in Roots and Nodules of Alnus glutinosa: I. Role of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase and Carbamyl Phosphate Synthetase in Dark CO(2) Fixation, Citrulline Synthesis, and N(2) Fixation. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):652–657. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting I. P., Dugger W. M., Jr Separation and detection of organic acids on silica gel. Anal Biochem. 1965 Sep;12(3):571–578. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance C. P., Stade S. Alfalfa Root Nodule Carbon Dioxide Fixation : II. Partial Purification and Characterization of Root Nodule Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):261–264. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance C. P., Stade S., Maxwell C. A. Alfalfa root nodule carbon dioxide fixation : I. Association with nitrogen fixation and incorporation into amino acids. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jun;72(2):469–473. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D., Van der Drift C. Differential analyses of glyoxylate derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jan;33(1):143–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wych R. D., Rains D. W. Simultaneous measurement of nitrogen fixation estimated by acetylene-ethylene assay and nitrate absorption by soybeans. Plant Physiol. 1978 Sep;62(3):443–448. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


