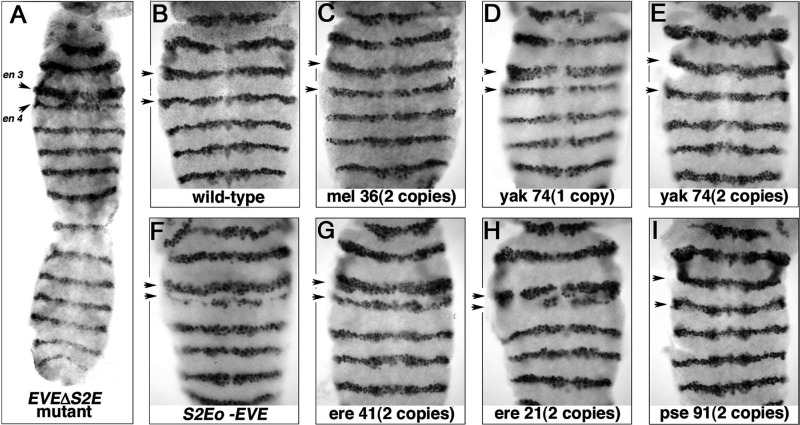
Figure 5. Effects on en Expression.
(A, C–I) The en pattern in homozygous EVEΔS2E and (B) wild-type (w1118) specimens at stages 9–11. All strains (except [B]) are homozygous for Df(eve) P(EVEΔS2E) second chromosomes, with the third chromosome differing only by rescue transgenes: (A) no rescue transgenes; (C) P(mel 36)/P(mel 36) is a S2Emel-EVE stock; (D) P(yak 74)/TM3 Sb and (E) P(yak 74)/P(yak 74) are S2E yak -EVE stocks; (F) P(S2Eo-EVE)/P(S2Eo-EVE) has no S2E; both (G) P(ere 41)/P(ere 41) and (H) P(ere 21)/P(ere 21) are S2Eere-EVE transgenic stocks; and (I) P(pse 91)/P(pse 91) is a S2Epse-EVE stock. Note the variation in distance between third and forth en stripes (arrows) and relative level of en expression in the fourth stripe. Only the first seven parasegments of the en pattern are show (except in [A]). The en protein was visualized by an immunoperoxidase DAB reaction enhanced by nickel. mel: D. melanogaster; yak: D. yakuba; ere: D. erecta; pse: D. pseudoobscura. S2Eo-EVE lacks a S2E.