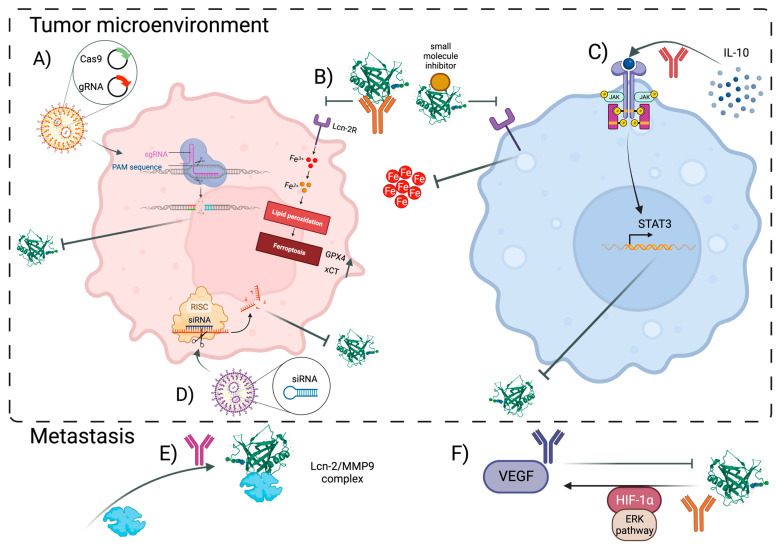
Figure 2.
Overview of the potential targeting strategies to block Lcn-2 functionality in both cancer cells (left panel) and macrophages (right panel) in the TME, but also to prevent metastasis. (A) CRISPR/Cas9 editing technique together with optimized nanocarriers can be used in research to study cancer cell-derived effect of Lcn-2 in tumor progression, and in the future as a therapeutic strategy. (B) Lcn-2 can be blocked by monoclonal antibodies and small-molecule inhibitors such as ZINC00784494 or ZINC00640089, potentially affecting iron availability, whereby the induction of ferroptosis in cancer cells, and stronger iron sequestration in macrophages, could be triggered. (C) Due to the strong upregulation of Lcn-2 upon IL-10 (an anti-inflammatory cytokine highly abundant in the TME) stimulation by macrophages, via STAT3 and C/EBPβ, it could be suggested that blocking IL-10 could reduce the expression of Lcn-2, ultimately preventing macrophage polarization towards an M2-like phenotype. (D) Similarly, as with (A), siRNA-mediated Lcn-2 could help unravel the role of Lcn-2 in carcinogenesis, which could be further translated into combinatorial therapy. Finally, since Lcn-2 contributes to invasion and metastasis, and angiogenesis, by binding to MMP9 and inducing HIF-1α and VEGF, respectively, targeting these complexes could be utilized to prevent further tumor development. (E) Destabilization of Lcn-2/MMP9 complex carcinoma led to decreased lung metastasis, while (F) blocking VEGF affected angiogenic activity of Lcn-2. However, Lcn-2 also induces VEGF mediated by HIF1α via the Erk pathway, which could be another Lcn-2-dependent mechanism used as a therapeutic approach [141,145,146,147,148,149]. Abbreviations: Lcn-2: Lipocalin-2, TME—tumor microenvironment, CRISPR/Cas9—clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9, STAT3—signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, C/EBPβ—CCAAT enhancer-binding proteins β, MMP9—matrix metalloprotease 9, HIF1α—hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, and VEGF—vascular endothelial growth factor. Created using BioRender.com.