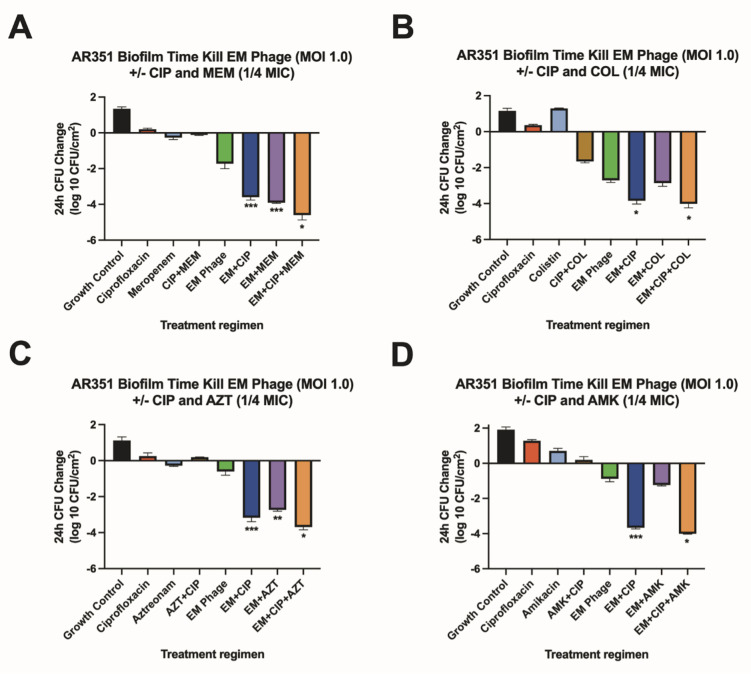
FIG 1.
Biofilm time-kill analyses for AR351. Biofilm time-kill analyses of CIP-COL, CIP-AZT, CIP-AMK, and CIP-MEM alone and in combination with EM-T3762626-2_AH (EM) phage against AR351 at 0.25× MIC (COL 0.25 µg/mL, AZT 16 µg/mL, AMK 16 µg/mL, CIP 0.25 µg/mL, and MEM 8 µg/mL) and a theoretical MOI of 1.0. Subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations are used to mimic the expected drug ineffectiveness that would otherwise not occur in this simplified in vitro system. The bars represent the difference in 24-h CFU/cm2 from baseline. (A) Strain AR351 versus ciprofloxacin (1/4 MIC) and/or meropenem (1/4 MIC) with and without phage EM (MOI 1.0). (B) Strain AR351 versus ciprofloxacin (1/4 MIC) and/or colistin (1/4 MIC) with and without phage EM (MOI 1.0). (C) Strain AR351 versus ciprofloxacin (1/4 MIC) and/ or aztreonam (1/4 MIC) with and without phage EM (MOI 1.0). (D) Strain RAR351 versus ciprofloxacin (1/4 MIC) and/or amikacin (1/4 MIC) with and without phage EM (MOI 1.0). Values are means ± standard deviations from two biological replicates. *Regimen(s) that demonstrated bactericidal activity. **Regimen(s) that demonstrated synergy. ***Regimen(s) that demonstrated both synergy and bactericidal activity. AMK, amikacin; AZT, aztreonam; CIP, ciprofloxacin; COL, colistin; EM, phage EM-T3762627-2_AH; MEM, meropenem; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; MOI, multiplicity of infection.