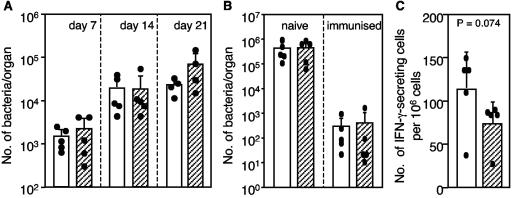
FIG. 5.
Effects of MDC-specific antiserum on in vivo anti-S. enterica serovar Typhimurium immune responses. Groups of five mice were injected i.p. with 0.5 ml of rabbit anti-MDC antiserum (cross-hatched bars) or isotype control anti-GST antiserum (open bars). The bars and error bars indicate the means and standard deviations, respectively, for each group of mice, and the solid dots indicate the values for individual mice. (A) On day zero, mice were injected i.p. with antiserum, and on day 1 mice were immunized intravenously with 100 CFU of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium BRD509. On days 7 and 14, two more injections of antiserum were administered. The bacterial load in each mouse spleen was determined by plating serial dilutions of spleen homogenates. (B) Naïve and BRD509-immunized mice were injected i.p. with antiserum 1 day prior to oral challenge infection with wild-type S. enterica serovar Typhimurium SL1344. On day 5 after the challenge, the bacterial load in each mouse spleen was determined by viability counting. (C) Effect of MDC neutralization on the number of IFN-γ-secreting cells present in the spleens of BRD509-immunized mice 3 days after challenge infection with SL1344 as determined by an ELISPOT assay. The nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test was used for statistical analysis.